Ever wondered how massive spaces like university campuses or sprawling retail stores manage to offer perfect Wi-Fi everywhere you go? Hey, it’s a great question! The secret sauce is often a mesh network. It’s like having a team of smart Wi-Fi access points all working together, chattering amongst themselves to create one big, unified, and powerful network.
The Foundations of Mesh Network Topologies

Let’s try a simple analogy. Imagine you need to get a message from one side of a busy city to the other. Instead of relying on a single, central post office, what if you had a network of couriers scattered everywhere? Each courier—or node—could pass the message to the next closest one, forming a web of potential routes. If one courier hits a dead-end or gets stuck in traffic, the message just hops to another one and finds a different way.
That’s the fundamental principle behind mesh network topologies. In the world of Wi-Fi, each of those "couriers" is a wireless access point. These devices talk directly to each other, automatically figuring out the best and most efficient path for your data to travel.
This built-in intelligence makes mesh networks incredibly reliable. If one access point happens to fail or go offline, the whole system doesn't grind to a halt. The other nodes simply reroute the traffic around the dead spot. The result? Your connection stays up and running, strong and stable.
Why This Design Matters Today
This idea of a decentralized, resilient network isn't exactly new. The concept of mesh network topologies actually has its roots in military research from the 1960s, which was focused on building communication systems that could withstand damage and keep operating.
Today, that same level of robustness is absolutely essential in places where connectivity is non-negotiable. Think about sectors like Education, Retail, and corporate environments that are flooded with personal devices (BYOD). This is why companies like Cisco bake this principle into their Cisco Meraki solutions—to deliver rock-solid Wi-Fi over huge areas. As organizations grapple with managing tons of personal devices, the conversation around modern network design is more relevant than ever.
This distributed approach is what unlocks the sophisticated features that modern businesses and institutions depend on.
A well-designed mesh network provides the foundation for advanced user management, ensuring that every connection is not just stable, but also secure and intelligently controlled.
Connecting Users Securely
With that stable foundation in place, modern mesh networks can then layer on powerful Authentication Solutions. When a student connects to campus Wi-Fi or a shopper logs into a store’s network via a Captive Portal, the underlying mesh makes sure their connection is smooth from start to finish.
Technologies like IPSK (Identity Pre-Shared Key) and EasyPSK take this security a step further. They allow you to assign unique credentials to every single user or device, giving you fine-grained control in a world full of personal gadgets. It’s this powerful combination of a reliable infrastructure and smart security that makes mesh networks the go-to choice for so many.
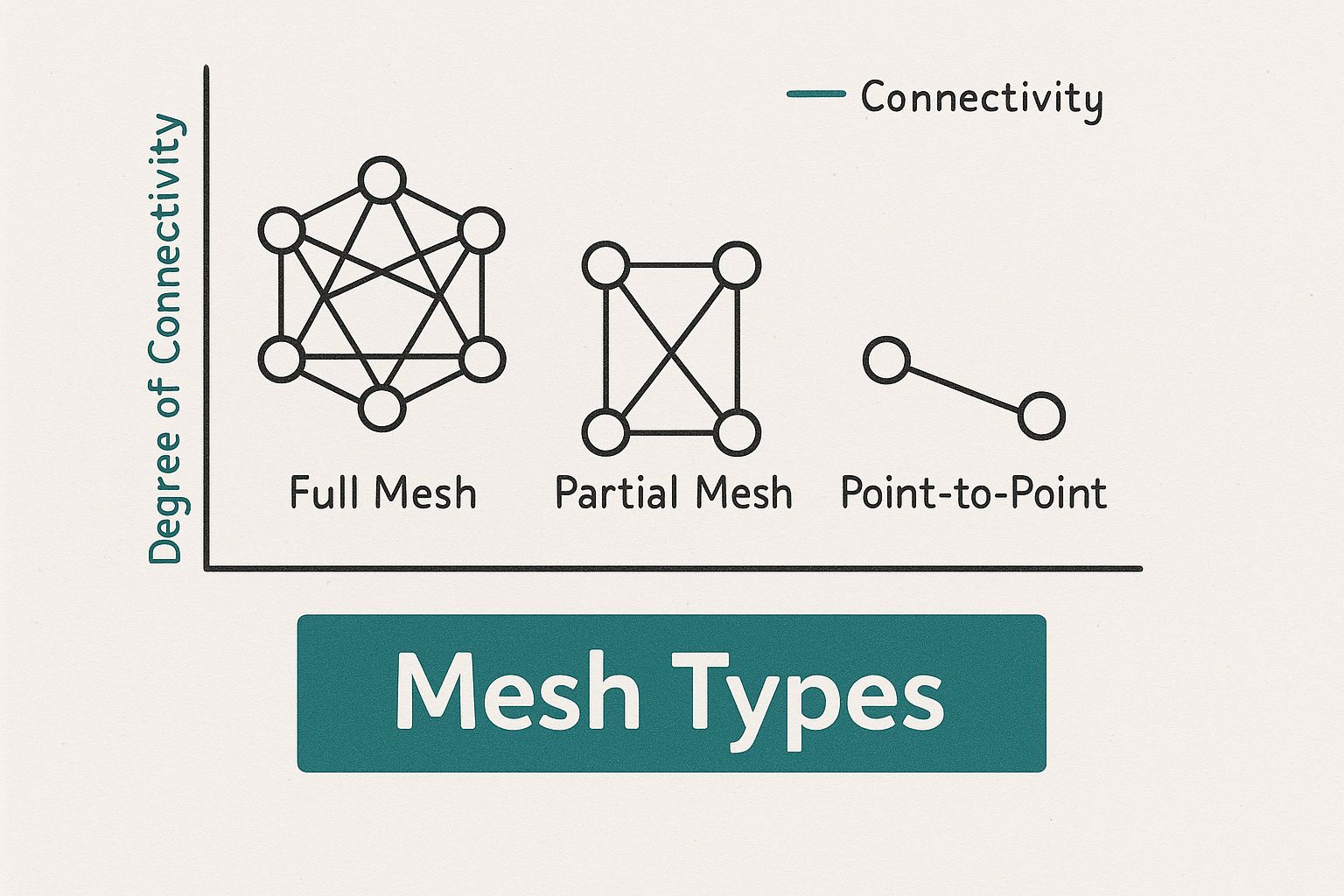
Full Mesh vs. Partial Mesh: Choosing Your Network's Blueprint
Now that we've covered the basics of how mesh networks operate like a team, let's get into the two main strategies, or "topologies," you can use: full mesh and partial mesh.
Think of these as the two fundamental blueprints for designing your network. The one you choose will have a major impact on everything from performance and cost to how well your network handles a sudden outage.
This diagram gives you a great visual for how these two structures differ.
You can immediately see the dense, all-to-all web of a full mesh versus the more selective, hub-and-spoke style connections in a partial mesh.
Full Mesh Topology: The All-In Approach
Imagine a small team where every single person can talk directly to everyone else without passing a message. That's a full mesh topology in a nutshell. Every access point (or node) in the network is directly connected to every other access point. This creates an incredibly dense web of connections.
What's the payoff? Unbeatable redundancy.
If one connection fails—or even if an entire access point goes offline—it’s just a minor hiccup. Data simply reroutes itself along one of the many other available paths. This makes full mesh networks unbelievably fault-tolerant. In high-stakes environments, like a corporate headquarters handling sensitive data, that kind of reliability is non-negotiable.
But this all-in approach has its downsides. The sheer number of connections required makes it complex and expensive to set up, especially as the network gets bigger. For a network with N devices, you need to create N(N-1)/2 links. The complexity just explodes with every new device you add.
Partial Mesh Topology: A Strategic Balance
This is where the partial mesh topology comes in, and it's by far the more common choice for most situations. Instead of connecting every node to every other node, only some nodes are fully interconnected, typically the most critical ones.
Think of it like an airline's route map. Major airports have direct flights to all other major airports, but smaller, regional airports only connect to the nearest major hub.
In a partial mesh, some nodes act as the backbone of the network, while others on the periphery connect to just one or two of these central points. This design strikes a really smart balance between reliability and cost. You still get the core self-healing benefits of a mesh network, but without the massive expense and complexity of a full mesh.
A partial mesh gives you a practical solution, putting robust connectivity where it matters most while keeping the budget and management complexity under control. It has become the go-to design for most large-scale Wi-Fi deployments today.
This balanced approach makes it a great fit for places like large Retail chains or sprawling Education campuses that need solid coverage without breaking the bank. Modern networking platforms, like those from Cisco Meraki, are built to manage these kinds of intelligent partial mesh networks, automatically finding the best data paths on the fly. For anyone tasked with designing a system that can handle interruptions, learning how to build a more resilient network with these concepts is crucial.
Full Mesh vs Partial Mesh At a Glance
So, when does one make more sense than the other? This table breaks down the key differences to help you decide which blueprint is right for your environment.
| Characteristic | Full Mesh Topology | Partial Mesh Topology |
|---|---|---|
| Connectivity | Every node connects to every other node. | Only some nodes connect to each other; often uses central hubs. |
| Redundancy | Extremely high. Many alternative paths if a link fails. | High, but lower than full mesh. Failure of a central node can be impactful. |
| Scalability | Poor. Complexity and cost grow exponentially. | Excellent. Easy to add new nodes without a massive overhaul. |
| Cost | Very high due to extensive cabling and hardware. | Moderate. Fewer connections mean lower hardware and installation costs. |
| Best For | Small, mission-critical networks (e.g., data center backbone). | Large-scale deployments (e.g., offices, schools, retail). |
Ultimately, picking the right topology comes down to weighing your need for absolute uptime against your budget and the scale of your project.
Making the Right Choice for Your Environment
So, which one should you choose? It really boils down to balancing your need for bulletproof reliability against what you're willing to spend and manage.
- Full Mesh excels in: Smaller environments where 100% uptime is the top priority and cost isn't the primary concern.
- Partial Mesh is ideal for: Most large-scale deployments, including corporate BYOD environments, schools, and retail spaces where you need a practical blend of high reliability and reasonable cost.
In the end, both topologies provide the resilient foundation needed for modern Authentication Solutions. Whether someone is logging in through a Captive Portal at a coffee shop or using an IPSK or EasyPSK key on a university campus, a well-designed mesh network ensures their connection is stable and seamless from the start.
Exploring Key Hybrid Mesh Network Designs
In a perfect world, we could just pick a single, tidy network design like a full or partial mesh and call it a day. But the real world is messy. It’s full of unique challenges that demand more flexible and practical solutions. This is exactly where hybrid mesh network designs shine, offering a "best-of-all-worlds" approach by blending different topologies.
Think of it like designing a city's transportation system. You wouldn't rely solely on buses for every trip. Instead, you’d use high-speed trains for long-haul routes (your network backbone), buses for local neighborhood circuits (a local mesh), and maybe ride-sharing services for direct point-to-point travel. A hybrid network does the same thing for data, combining the strengths of mesh, star, and other designs to create a powerful, custom-fit system.
This approach gives you the power to build a network that’s perfectly shaped for the demands of any environment, whether it's a sprawling university campus or a massive, multi-level shopping mall.
Building a Smarter Network with Hybrid Designs
A classic example of a hybrid design involves using a powerful, high-speed wired backbone—often in a bus or star topology—to connect different buildings or floors. Then, within each of those zones, you can deploy a wireless partial mesh network to deliver flexible and resilient local coverage.
This structure gives you the rock-solid stability and sheer speed of a wired connection right where it matters most. At the same time, you get the self-healing and easy scalability of a wireless mesh where you need it.
For instance, picture a large corporate office with a heavy BYOD (Bring Your Own Device) policy. The main server room and the links between departments might run on a super-fast fiber backbone. But within each department's open-plan workspace, a series of Cisco Meraki access points could form their own local mesh. If one AP in the marketing department goes down, it won’t have any impact on the finance team’s connectivity.
Orchestrating this kind of intelligent architecture has become much simpler thanks to modern management platforms. By exploring what software-defined networking is, you'll see how centralized controllers can manage these complex, multi-topology environments from a single pane of glass.
A hybrid mesh topology isn't just a compromise; it's a strategic decision. It allows you to invest in high-cost, high-performance infrastructure where it's absolutely critical, while using cost-effective, flexible solutions everywhere else.
Hybrid Topologies in Action Across Different Sectors
The real beauty of hybrid mesh network topologies is their versatility. They can be molded to solve very specific challenges across all sorts of industries, especially those dealing with large areas and a high density of users.
-
Education Campuses: A university might connect its library, dorms, and lecture halls with a high-speed fiber ring. Inside each building, a dense partial mesh of access points handles the thousands of student and faculty devices, ensuring reliable connectivity for everything from online exams to video streaming.
-
Retail Shopping Centers: A central wired network can connect all the storefronts and common areas back to the main internet gateway. The public Wi-Fi offered to shoppers can then be a large-scale wireless mesh, supporting Captive Portals for marketing and enabling seamless roaming as people wander from store to store.
-
Corporate Environments: Large corporations often use a hybrid model to support their extensive BYOD programs. A stable wired backbone ensures business-critical operations never falter, while a wireless mesh provides the flexibility for employees to work from conference rooms, common areas, and their desks without a hitch.
This adaptability is also crucial for deploying advanced Authentication Solutions. When a user connects, their experience has to feel seamless, whether their data is traveling over a wired link or hopping between wireless nodes. Hybrid designs, managed by platforms like Cisco Meraki, ensure this consistency. They provide the stable foundation needed for security protocols like IPSK and EasyPSK, which assign unique keys to each device for secure, controlled access across the entire network—no matter its underlying physical structure.
Mesh Networks in Education and Retail
Let’s move past the theory and look at where these mesh network topologies really shine. Two areas that absolutely live or die by their connectivity are Education and Retail. In these busy environments, a single Wi-Fi dead zone can mean a student bombs an online exam or a shopper walks out without making a purchase.
For schools, colleges, and universities, reliable Wi-Fi isn't just a perk anymore—it's the foundation of modern learning. Everything from digital classrooms and online testing to group projects and campus communications depends on a solid network. This is where a hybrid mesh network becomes the perfect solution, creating a resilient blanket of connectivity across the entire campus.
This setup ensures students and staff have a solid connection, whether they’re in a historic lecture hall, a state-of-the-art science lab, or just hanging out on the campus quad. The network has to juggle thousands of simultaneous connections from laptops, tablets, and phones, making the BYOD (Bring Your Own Device) culture work smoothly and securely.
Powering the Modern Campus
Picture a sprawling university campus. A high-speed wired backbone might link the main library, administration building, and various faculty departments. Then, inside each of those buildings, a dense wireless partial mesh, perhaps using access points from a system like Cisco Meraki, can handle the heavy traffic from all the devices.
The beauty of this design is its resilience. If an access point in a packed student union suddenly goes down, the other nodes in the mesh instantly find new routes for the data. The students cramming for finals won't even notice a hiccup. That self-healing ability is what keeps a digital learning environment stable.
In an educational setting, network downtime isn't just an inconvenience; it can directly impact student success. Mesh networks provide the fault tolerance needed to keep digital learning on track, no matter what.
On top of this solid foundation, schools can add powerful Authentication Solutions. Captive Portals are great for welcoming new students and visitors, walking them through a simple and secure onboarding process. For everyday access, technologies like IPSK (Identity Pre-Shared Key) and EasyPSK are fantastic, giving each student and faculty member their own unique, private key for all their personal devices.
Transforming the Retail Experience
Now, let's switch gears to the fast-moving world of Retail. Here, a mesh network pulls double duty. First, it gives shoppers the seamless Wi-Fi experience they've come to expect, which is proven to keep them in the store longer. Second, and just as important, it powers the internal tools that keep the business running smoothly.
Modern retailers depend on Wi-Fi for just about everything:
- Point-of-Sale (POS) Systems: Mobile POS terminals let associates check out customers anywhere on the floor, killing long lines.
- Inventory Management: Staff can use handheld scanners to track stock in real-time, from the backroom to the shelf.
- Customer Engagement: Associates use tablets to look up product info or show customers different styles and options.
A partial mesh network is ideal for ensuring these critical tools stay connected as employees move around the store. If a new display or shelving unit temporarily blocks an access point, the network just finds another path. No big deal.
Beyond just providing a connection, systems from vendors like Cisco Meraki can turn a guest network into a smart business tool. When shoppers log in through a Captive Portal, retailers can show them targeted promotions, offer special discounts, or invite them to a loyalty program. It's one of the best ways retailers can make the most of their wireless deployments, transforming a simple utility into a direct line of communication with customers. You can discover more about how retailers can leverage their wireless deployments in our detailed guide.
Whether it’s a student submitting an essay at the last minute or a shopper comparing prices in an aisle, mesh topologies provide the reliable, secure, and intelligent networking needed for today's world.
Securing Your Network in BYOD Environments
In the modern workplace, the lines between personal and work devices have completely blurred. The rise of BYOD (Bring Your Own Device) policies is everywhere—from Corporate offices and Education campuses to Retail stores. This shift creates a massive headache for anyone managing a network: How do you offer simple, reliable Wi-Fi for everyone's devices without swinging the doors wide open to security threats?
The old way of doing things—a single Wi-Fi password for the entire organization—just doesn’t cut it anymore. Modern Authentication Solutions, especially when layered on top of a resilient Cisco Meraki mesh network, are designed for this exact challenge. The real goal is to make connecting feel effortless for the user while being incredibly secure behind the scenes.
This is where a technology called IPSK (Identity Pre-Shared Key) completely changes the game. Imagine a traditional Wi-Fi password as a single master key for an entire office building. If one person shares it or loses it, the whole building is compromised. IPSK, and similar solutions like EasyPSK, work differently. It’s like giving every single employee their own unique key to the building.
The Power of Individual Keys
With an IPSK system, every user or device gets its own private credential to get on the network. This simple change brings huge security advantages.
For instance, when an employee leaves the company, you no longer have to change the Wi-Fi password for everyone else and deal with the fallout. You just revoke that one person's key, and their access is cut off instantly. This kind of granular control is crucial for managing the constant flow of devices connecting and disconnecting from your network.
This approach also gives you a much clearer picture of what's happening on your network. Since every device has its own key, you can see exactly who is connected at any given time. This visibility is vital for troubleshooting problems or spotting any strange activity before it becomes a real issue. For more on building a solid BYOD framework, check out our guide on developing a bring-your-own-devices policy.
In a BYOD environment, security isn't just about keeping threats out; it's about knowing exactly who is on your network at all times. IPSK provides that critical layer of identity-based control.
Streamlining Security with Cisco Meraki
So, managing thousands of unique keys sounds like a logistical nightmare, right? Actually, it's not. Powerful platforms like Cisco Meraki make it surprisingly simple. Through Meraki's cloud dashboard, an administrator can roll out and manage an IPSK solution across the entire organization with just a few clicks.
You can set it up to automatically generate unique keys for new users, create temporary keys that expire for guests or contractors, and even sync it with your existing employee directories. This automation removes all the heavy lifting from securing a large-scale BYOD environment.
- For Corporate Offices: When a new hire starts, a unique key can be automatically generated for all of their devices, ensuring they can only access the resources they’re approved for.
- In Education: A student can get a single, secure key that works on their laptop, phone, and tablet for the whole school year, with access automatically revoked when they graduate.
- For Retail Staff: Employees can get secure access to internal tools like inventory scanners and mobile POS systems, keeping that sensitive traffic completely separate from the public guest Wi-Fi.
This combination of a solid mesh network foundation and smart authentication creates a secure, fast experience for everyone. In these settings, establishing a secure network setup for remote access is also essential, allowing authorized users to connect to internal resources safely from anywhere.
The Role of Captive Portals
IPSK is the perfect solution for trusted users like employees and students, but what about visitors? This is where Captive Portals still shine. When you integrate a captive portal into a Cisco mesh network, it gives you a branded, professional landing page for guests to connect.
This not only secures guest access but also gives you an opportunity to display your terms of service or share promotional messages. By pairing IPSK for your internal team with Captive Portals for guests, you create a layered security strategy that covers every person and every device, protecting your data while keeping everyone connected.
Frequently Asked Questions About Mesh Topologies
It's completely normal to have questions when you're digging into mesh network topologies. As you start mapping out a Wi-Fi solution that needs to be rock-solid, a few things might still feel a bit fuzzy. To clear things up, I’ve put together answers to some of the most common questions we hear.
The goal here is to help you feel confident about your next steps, whether you're designing a network for a busy school campus, a large retail store, or a corporate office packed with personal devices.
What Is the Main Advantage of a Mesh Topology?
If you take away only one thing, let it be this: the biggest advantage of a mesh network is its incredible reliability through redundancy. Think of it as having built-in detours for your data. In a more traditional network, if a key piece of hardware like a central switch or a single access point fails, it can create a massive dead zone.
Mesh networks get around this because their access points (or nodes) can all talk directly to each other. If one node suddenly goes offline, the others intelligently find a new path for the traffic, routing it around the problem area. This "self-healing" ability makes mesh networks unbelievably resilient—a must-have for places like Education and Retail where consistent connectivity is everything.
How Does Mesh Wi-Fi Handle User Authentication?
This is a great question because the mesh topology itself is just the foundation. The real magic for managing who gets online comes from the Authentication Solutions built on top of it. For guest access, this is usually a Captive Portal. When someone new connects, they're guided to a branded landing page to agree to your terms, enter an email, or maybe even see a promotion before they can start browsing.
For trusted users in a BYOD Corporate environment, the methods get more sophisticated. Here, technologies like IPSK or EasyPSK come into play, giving each person or device its own unique Wi-Fi password. This gives you incredibly detailed control. If an employee leaves or a device is lost, you can instantly revoke that one specific key without affecting anyone else on the network.
The beauty of modern mesh systems, like those from Cisco, is how seamlessly they integrate these authentication layers. The underlying topology ensures the connection is stable, while solutions like IPSK ensure it’s secure and personalized.
Are Mesh Networks Difficult to Set Up?
That’s a common myth, and it’s understandable because the first generation of mesh systems could be a real headache to configure. Thankfully, those days are long gone. Modern platforms, especially cloud-managed ones like Cisco Meraki, have made the setup process astonishingly simple.
Most of the heavy lifting is completely automated. You plug in the Meraki access points, and they immediately start discovering each other to form the mesh. From there, a single cloud dashboard is your command center for configuring the entire network, checking its health, and managing users—no need to be a networking guru. This plug-and-play feel has made deploying large-scale mesh networks a reality for all kinds of organizations.

Can I Mix Wired and Wireless in a Mesh Network?
Absolutely! In fact, mixing them is one of the smartest and most common designs out there, often called a hybrid topology. Many of the most effective mesh network topologies rely on a high-speed wired backbone—like fiber or Ethernet—to connect different buildings or major zones.
Then, within each of those zones, a wireless mesh takes over to provide flexible, gap-free coverage. Picture a university campus: it might use a wired backbone to link the library, dorms, and lecture halls. Inside each of those buildings, a wireless mesh ensures students and faculty have a perfect connection everywhere. This hybrid strategy truly gives you the best of both worlds: the raw speed of a wired network and the adaptive reliability of wireless mesh.
How Secure Is a Mesh Network Really?
A mesh network is just as secure as any other network design—its safety comes down to the security measures you layer on top of it. The mesh structure itself, with all its different data paths, doesn't introduce new security holes. However, because it's so distributed, having strong security practices is even more critical.
This is exactly why you need to pair a mesh network with powerful Authentication Solutions.
- For Internal Users: Using IPSK or EasyPSK ties every connection to a specific person or device, making it simple to monitor and control access.
- For Guests: A well-configured Captive Portal keeps guest traffic completely separate from your internal network, so visitors can’t access sensitive company data.
- For Management: Platforms like Cisco Meraki come with built-in security tools like firewalls, traffic shaping, and intrusion detection to guard the entire network against threats.
When you do it right, a mesh network in a Corporate, Education, or Retail setting can be incredibly secure, creating a safe connection for both your internal resources and your users' devices.
What's the Difference Between a Mesh Network and Wi-Fi Extenders?
This is a fantastic question, because on the surface, they seem to solve the same problem: getting rid of Wi-Fi dead spots. But they go about it in completely different ways. A Wi-Fi extender is a pretty basic device. It just listens for your main router's signal and rebroadcasts it, creating a second, separate network. Your phone or laptop has to manually jump between the two, which often causes frustrating connection drops.
A mesh network, on the other hand, is a single, intelligent system. All the nodes work together as a team to create one seamless Wi-Fi network with a single name (SSID). As you walk around, your device is automatically and smoothly handed off to whichever node has the strongest signal, so you never feel a hiccup. It’s a far more sophisticated and elegant solution for true wall-to-wall coverage.
Ready to build a powerful, secure, and seamless Wi-Fi experience for your users? Splash Access integrates directly with Cisco Meraki to deliver best-in-class captive portals and authentication solutions. From secure IPSK for your internal teams to engaging splash pages for your guests, we make managing your network effortless. Learn more and see how we can transform your connectivity at Splash Access.