Ever find yourself staring at a loading screen, wondering what's really going on with your Wi-Fi? The answer often comes down to bandwidth. So, what is it? Think of bandwidth as the absolute maximum speed your wireless network could possibly achieve. It's the upper limit, the best-case scenario for how much data can move across your network at any given moment.
Your Wi-Fi Network is a Data Highway
Let’s ditch the technical-speak and use an analogy that makes perfect sense. Picture your Wi-Fi network as a multi-lane highway, and all the data zipping to and from your devices—laptops, phones, tablets—are the cars and trucks on that highway.
In this scenario, bandwidth is the total number of lanes. A narrow, two-lane road gets clogged up fast, causing a digital traffic jam. But a wide, eight-lane superhighway? It can handle a ton of traffic moving at top speed without anyone having to hit the brakes. Technically speaking, bandwidth is the maximum amount of data that can be sent over a wireless connection in a set amount of time, usually measured in megabits per second (Mbps) or gigabits per second (Gbps).
This isn't just theory; it's a critical factor in any busy venue. Imagine a university campus in the Education sector where every student is streaming lectures, a Retail store offering guest Wi-Fi to hundreds of shoppers, or a BYOD Corporate office where seamless video calls are non-negotiable. Without enough "lanes," every single online activity competes for the same limited space, and everything slows to a crawl for everyone.
Getting to Know the Key Terms
To really get a handle on network performance, we need to look beyond just bandwidth. A few other terms are just as important. Let's head back to our data highway to see how they all fit together.
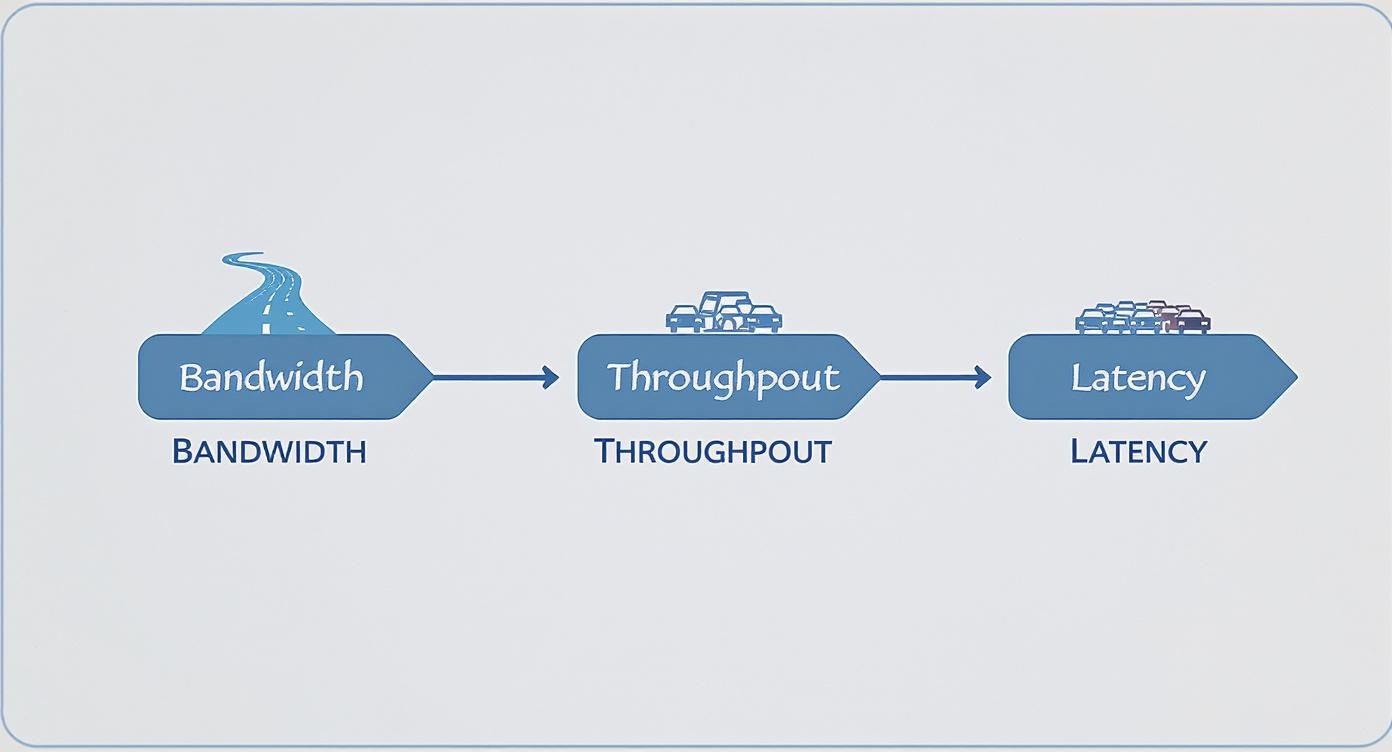
To make this crystal clear, here’s a quick breakdown using our highway analogy.
Bandwidth vs Throughput vs Latency At a Glance
| Term | Highway Analogy | What It Means for Your Wi-Fi |
|---|---|---|
| Bandwidth | The number of lanes on the highway | The maximum theoretical speed of your network. |
| Throughput | The actual number of cars passing a point per hour | The real-world speed you actually experience. |
| Latency | An unexpected traffic jam or red light | The delay or "lag" you feel during video calls or gaming. |
As you can see, the theoretical maximum (bandwidth) and your actual experience (throughput) can be two very different things.
Understanding these differences is the first step toward building a Wi-Fi network that doesn't just work, but works brilliantly. The physical hardware, like the access points that power your network, serves as the on-ramps and off-ramps to this data superhighway.
For any modern business, managing this digital traffic is essential. This is where powerful solutions from providers like Cisco Meraki come in. When you pair their hardware with smart Authentication Solutions like a Captive Portal using IPSK or EasyPSK, you essentially become the network's traffic controller. You can create express lanes for mission-critical business apps while ensuring guest or student traffic flows smoothly in its own lane, preventing congestion for everyone.
Factors That Determine Your Real-World WiFi Speeds
Ever feel like the Wi-Fi speed you pay for and the speed you actually get are two different things? You’re not just imagining it. While bandwidth represents the maximum potential of your network—the total width of your data highway—your real-world performance is all about the actual "road conditions."
Several key factors dictate how smoothly traffic flows. Think of them as the rules of the road, the number of lanes available, and the unexpected traffic jams that can slow everything to a crawl. Getting a handle on these variables is the first step toward building a wireless network that truly performs.
This visual helps break down the core ideas of bandwidth, throughput, and latency using that same highway analogy.
As you can see, your theoretical capacity (bandwidth) is often much higher than your actual speed (throughput) because of those real-world delays (latency).
The Rules of the Road: Wi-Fi Standards
Wi-Fi standards, like Wi-Fi 6 (802.11ax), are the official traffic laws governing your network. Each new generation brings major upgrades in speed, efficiency, and the ability to handle more devices at once.
Moving to a newer standard is like modernizing an entire highway system—it allows for higher speed limits and smarter traffic management. For instance, Wi-Fi 6 introduced features specifically designed for high-density environments like a lecture hall in an education setting or a packed retail store. You can dive deeper into how different standards stack up in our detailed guide on 802.11ac vs 802.11n.
Wider Lanes for More Data: Channel Width
If Wi-Fi standards are the laws, channel width is how many lanes each road has. Measured in megahertz (MHz), wider channels (80 MHz or 160 MHz) let more data travel at the same time, leading to much faster speeds for individual devices.
But there’s a catch. Using wider channels means you’re taking up a bigger chunk of the available radio spectrum, which can increase the potential for interference from neighboring networks. It's a trade-off that requires careful planning, especially in crowded wireless areas.
In dense deployments, such as a BYOD corporate office, balancing channel width is crucial. Professional-grade hardware, like Cisco Meraki access points, can automatically select the optimal channel width to maximize performance while minimizing interference.
Roadblocks and Traffic Jams: Interference and Obstacles
Wireless interference is the number one culprit behind poor Wi-Fi performance. It's the digital version of traffic jams, roadblocks, and accidents clogging up your data highway.
Common sources of interference include:
- Other Wi-Fi Networks: In an apartment building or a dense office park, your neighbors' networks are all competing for the same limited airtime.
- Household Appliances: Devices like microwaves, cordless phones, and even some Bluetooth speakers operate on the same 2.4 GHz frequency and can disrupt your signal.
- Physical Barriers: Concrete walls, metal filing cabinets, and even large crowds of people can absorb and reflect Wi-Fi signals, creating dead zones.
Too Many Cars on the Road: Client Density
Finally, the sheer number of devices connected to an access point—known as client density—plays a massive role. A single access point can only talk to so many devices at once. In a crowded university common area or a busy retail store during a sale, an underpowered network will quickly get bogged down.
This is where enterprise-grade solutions really prove their worth. A robust Cisco network is built to handle high client density, ensuring performance stays stable even when hundreds of users connect. When you pair that with smart authentication solutions and Captive Portals using IPSK or EasyPSK, you can effectively manage all that traffic and guarantee a smooth, secure connection for every student, shopper, or employee.
How Captive Portals Manage User Bandwidth
That login screen you see at a coffee shop or hotel? That's a Captive Portal, and it does a lot more than just ask for your email. Think of it as the digital gatekeeper for the network, a smart traffic cop deciding who gets in and, crucially, how much of your valuable bandwidth they get to use.
For any business, this level of control is essential. Without it, your guest Wi-Fi becomes a free-for-all. A few data-hungry users streaming 4K video could gobble up all the available bandwidth, leaving everyone else with a slow, frustrating, and unusable connection.
This is where advanced Authentication Solutions step in. They transform a simple Wi-Fi network into a managed, secure, and tiered service, making sure your most important digital traffic always gets the green light.
Creating Private Lanes on Your Wi-Fi Highway
Let's go back to our highway analogy. A Captive Portal lets you paint different lanes on that highway and set a unique speed limit for each one. This kind of segmentation is a game-changer in places with mixed user groups, like in Education, Retail, and corporate BYOD environments.
Modern systems pull this off using smart authentication methods that are a world away from a single, shared password. Instead, they grant network access based on who the user is or what their role is.
- Identity Pre-Shared Key (IPSK): This clever approach gives each user or device its own unique key to the network. It's perfect for corporate settings where you can assign different bandwidth profiles to employees, contractors, or even IoT devices. The executive team's video conferencing, for instance, can be routed into its own high-speed, high-priority lane.
- EasyPSK: This streamlines the whole onboarding process, especially in large-scale BYOD environments or on a school campus. New users can register their own devices through the portal, and they're automatically dropped into the right network segment with the correct bandwidth rules—no constant IT hand-holding required.
A university can use these methods to automatically place faculty and students on a fast, secure network while shunting campus guests to a separate, bandwidth-limited lane. This ensures critical academic resources are always snappy, no matter how many visitors are browsing Instagram.
Real-World Bandwidth Management in Action
Powerful networking gear from providers like Cisco Meraki, paired with a flexible management platform, makes this fine-grained control a reality. The portal isn't just a login page; it's an integrated part of your network's brain. You can discover more about setting up a WiFi Captive Portal in our complete guide.
In a Retail setting, this means your point-of-sale systems never have to fight for bandwidth with customers streaming videos in the aisle. You can put the POS devices on their own private, high-priority virtual network, ensuring transactions fly through instantly, every time.
Likewise, in a corporate office with a BYOD policy, you can use IPSK to create different access tiers. Company-owned laptops could get unlimited bandwidth, while employees' personal smartphones get a generous but capped amount. It’s a smart way to balance convenience with protecting bandwidth for mission-critical operations.
Ultimately, a Cisco-powered network with an intelligent captive portal elevates your Wi-Fi from a simple utility to a strategic asset. It lets you define precisely who gets on, what they can access, and how much bandwidth they can use, guaranteeing a top-notch connection for the people and applications that keep your organization running.
Getting a Grip on Your WiFi Network’s Real-World Performance
Knowing the theory behind bandwidth and throughput is great, but the real win comes from taking control of your network’s actual, day-to-day performance. For any IT manager or business owner, the goal isn't just to have Wi-Fi; it's to have Wi-Fi that’s a rock-solid asset for your operations. This means you have to look beyond a simple internet speed test and get your hands dirty with how your network is truly behaving on the inside.
When you actively measure and optimize, you start to see the whole picture. You can hunt down bottlenecks, wipe out dead zones, and make sure your most critical applications always get the priority they need to run flawlessly. This is non-negotiable in a busy corporate office with a BYOD policy, a sprawling university campus in the Education sector, or a Retail store where the customer experience is everything.
Measuring What Actually Matters
First thing's first: a standard internet speed test only tells you a fraction of the story. It’s measuring the connection from your router to the big, wide world of the internet. That's useful, sure, but it tells you nothing about how efficiently data is zipping around inside your building—from an access point to a user's laptop. That internal speed is your real Wi-Fi throughput.
To get an accurate picture, you need tools that are built to measure local network performance. This usually involves a few key steps:
- Network Analysis Tools: Software like
iperf3is a fantastic way to measure the maximum speed between two devices on your own network. This helps you find internal slowdowns without your internet provider's connection muddying the waters. - Wi-Fi Analyzers: These apps are like a window into the invisible world of radio waves. They scan your environment and show you exactly which Wi-Fi channels are jam-packed with traffic, which is pure gold for dodging interference from your neighbors.
- Heat Mapping: A professional site survey generates a "heat map" of your building, giving you a visual floor plan of your signal strength. It’s the single best way to spot those frustrating dead zones and figure out how to fix them.
Once you’ve got this data, you can start making smart, targeted improvements. Maybe a specific conference room has a weak signal, or you discover your channels are completely overcrowded. For more practical advice on this, our guide on how to check bandwidth used by devices offers some great next steps.
Smart Moves for Peak Performance
With a clear diagnosis of your network's health, you can shift to optimization. This isn't about throwing money at a faster internet plan; it’s about using the bandwidth you already have more intelligently. A well-managed network, especially one built on hardware like Cisco Meraki, gives you the granular control you need to make these powerful tweaks.
Here are a few of the most effective strategies you can use:
1. Place Your Access Points (APs) Wisely
Where you put your APs has a huge impact on coverage and speed. Don't just tuck them away in a supply closet or mount them behind a concrete pillar and hope for the best. A proper site survey will reveal the ideal spots to ensure a strong, consistent signal fills your entire space, whether it's a multi-floor office building or a wide-open retail showroom.
2. Make Intelligent Channel Choices
Most Wi-Fi networks are left on the "auto" channel setting, which can easily lead to a traffic jam if other nearby networks are using the same channels. Using a Wi-Fi analyzer, you can manually select less congested channels, particularly in the cleaner 5 GHz band. Even better, enterprise-grade systems from providers like Cisco often handle this dynamically, constantly scanning for interference and hopping to a clearer channel to keep things running smoothly.
By setting specific Quality of Service (QoS) rules, an administrator can ensure that a retail store’s point-of-sale (POS) terminals and a corporate office’s video calls are always given the highest priority, preventing them from ever being slowed down by less important traffic.
3. Put Quality of Service (QoS) to Work
Think of Quality of Service as your network’s bouncer—it decides who gets to go first. This feature lets you tell your router which types of data are VIPs. For example, in an Education venue, you can give top priority to video conferencing for remote classes, while pushing students' social media traffic to the back of the line.
With an intuitive platform like the Cisco Meraki dashboard, setting these rules is surprisingly simple. You can create traffic-shaping policies that reserve a certain amount of bandwidth for specific apps or user groups. When you combine this with powerful Authentication Solutions like IPSK or EasyPSK, you gain incredibly precise control over your network. This is what transforms a basic Wi-Fi network into a high-performance business tool.
Different Industries, Different Wi-Fi Needs
When it comes to Wi-Fi, there’s no magic bullet. A university lecture hall has completely different bandwidth demands than a small coffee shop or a secure corporate office. The secret to delivering a great wireless experience is to stop thinking in terms of a one-size-fits-all network and start designing for your specific environment.
This is where a thoughtful strategy, powered by capable hardware like Cisco Meraki access points and smart Authentication Solutions, really makes a difference. By creating specific rules for different users and applications, you can make sure your network’s resources go exactly where they’re needed most. Let's look at a few common scenarios to see how this plays out.
High-Density Networks for Education
Nowhere is the client density challenge more real than in Education. A modern campus is a bustling ecosystem of thousands of devices—laptops, tablets, and smartphones all fighting for airtime. In a single large lecture, you could have hundreds of students streaming video, downloading course materials, and collaborating on projects at the same time.
In this high-stakes BYOD (Bring Your Own Device) world, just having a lot of bandwidth isn’t the full story. The network has to be smart enough to get all those devices connected securely and without creating a headache for the IT department.
This is a perfect job for EasyPSK. Instead of a single campus-wide password that’s easy to share and compromise, students and staff can register their own devices through a branded Captive Portal. Once they authenticate, their device gets a unique key and is automatically placed on the right network segment. This approach dramatically cuts down the IT workload while creating a much safer and more reliable network for everyone.
Seamless Guest Experiences in Retail
For a Retail business, Wi-Fi wears two hats. First, it's essential for operations, running everything from point-of-sale (POS) systems to inventory scanners. Second, it's a customer perk that can make the shopping experience much better. The trick is to ensure the guest network never slows down the business-critical traffic.
A well-designed Captive Portal is the key. It’s the front door for guest access, and many shops use it to show off special deals or gather marketing opt-ins. But behind the scenes, an administrator can set firm bandwidth limits for shoppers. This guarantees that a few customers streaming videos won’t bring credit card transactions to a crawl.
This separation is crucial. By putting POS terminals and employee devices on a separate, high-priority virtual network, a retailer can protect its most important traffic. Customer Wi-Fi remains a great perk, but the core business keeps humming along without a problem.
Balancing Security and Convenience in Corporate Offices
The modern BYOD Corporate office is a constant balancing act between employee freedom and ironclad security. People expect to connect their personal devices without a hassle, but the IT team must protect sensitive company data and make sure essential business apps always have the bandwidth they need.
This is where a solution like IPSK (Identity Pre-Shared Key) really shines. When integrated with a Cisco network, IPSK gives administrators the power to assign unique credentials and network policies based on a user’s role.
- Executives might get unlimited bandwidth and priority access to ensure their video conferences are always crystal clear.
- Full-time employees could receive generous bandwidth on their company laptops for everyday work.
- Contractors and guests can be firewalled onto an isolated network with limited bandwidth and no access to internal files.
This level of granular control means bandwidth is distributed intelligently, aligning network performance directly with business goals. For a deeper dive into building the right network for your organization, check out our guide on finding the best WiFi solutions for business.
For businesses in the medical field, where the seamless flow of information is non-negotiable, understanding the principles of data interoperability in healthcare is just as critical. By applying these industry-specific strategies, a Wi-Fi network becomes more than just a utility—it becomes a strategic asset that helps you achieve your core mission.
Common Questions About WiFi Bandwidth
Let's dig into some of the most common questions we hear about WiFi performance. Getting these answers right can make a huge difference in how you plan, manage, and grow your network, whether it’s for a bustling retail space, a sprawling campus, or a corporate office.
How Much WiFi Bandwidth Does My Business Need?
This is the big one, but there's no magic number. The right answer really depends on two things: how many people are using your network and what they're actually doing online.
A small coffee shop might get by perfectly with a 100 Mbps connection. On the other hand, a high-density university campus supporting a massive BYOD program could easily need 1 Gbps or more. As a starting point, try to budget about 5-10 Mbps per user for basic activities like browsing and email. For more intensive stuff, like video streaming or online learning in an Education setting, you'll want to aim for 25-50 Mbps per person.
This is where professional network management tools really shine. An ecosystem like Cisco Meraki gives you incredible insight into how your bandwidth is being used, helping you accurately size your needs today and plan for growth tomorrow.
Will a Captive Portal Slow Down My WiFi?
This is a very common worry, but the short answer is no. A well-configured Captive Portal has virtually zero impact on your WiFi speed. The initial login process is just a quick, one-time digital handshake to get someone connected.
What a portal does give you is control over network policies after that handshake. For example, using a portal to limit guest users in a Retail store to 5 Mbps each isn't a bug—it's a powerful feature. It guarantees that your guest WiFi doesn't hog all the bandwidth needed for critical business operations, like your point-of-sale systems.
Authentication Solutions like IPSK or EasyPSK take this even further. They can make the authentication process completely invisible for trusted devices after their first connection, blending top-notch security with a seamless user experience.
Can I Improve WiFi Performance Without Paying My ISP More?
Absolutely. Think of your ISP plan as the maximum amount of water flowing into your building through a big pipe. How well you distribute that water internally is a completely different story.
You can often see massive improvements without ever upgrading your internet package. Key strategies include:
- Upgrading Your Gear: Moving to modern Wi-Fi 6/6E access points can dramatically boost efficiency and speed for compatible devices.
- Optimizing AP Placement: A proper radio frequency (RF) survey helps you find the perfect spots for your APs, killing dead zones and ensuring strong coverage.
- Managing Your Channels: Manually selecting less-congested WiFi channels helps you sidestep interference from neighboring networks.
- Prioritizing Key Traffic: Using Quality of Service (QoS) rules tells your network to give critical applications first dibs on bandwidth, so they always run smoothly.
These are all about making the most of the bandwidth you already pay for.
What Is the Difference Between 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz WiFi?
Think of them as different highways for your data.
The 2.4 GHz band is like an old, two-lane country road. It can go a long way, but it gets crowded easily. It’s often congested with interference from other WiFi networks and even common devices like microwaves, which means slower speeds.
The 5 GHz band (and the newer 6 GHz band) is a modern superhighway with tons of lanes and far less traffic. It delivers much faster speeds but doesn't have quite the same reach as the 2.4 GHz band.
Modern network systems from providers like Cisco use a smart feature called "band steering." This automatically nudges capable devices onto the faster, cleaner 5 GHz or 6 GHz bands, making sure they get the best connection possible without the user having to do a thing.
Ready to take full control of your network's bandwidth and create a superior user experience? Splash Access integrates seamlessly with Cisco Meraki to deliver powerful, customizable captive portals and advanced authentication solutions. Explore what's possible at https://www.splashaccess.com.