Hey there! If you're responsible for the Wi-Fi in a commercial space, you know it's about more than just providing a connection. You're on the front line of network defense. Getting Wi-Fi security right is the bedrock of a safe, reliable digital experience for your customers, students, or employees. This guide will walk you through exactly how to build a secure wireless environment that protects everyone who connects.
Why Modern WiFi Security Is No Longer Optional

Let's cut to the chase: a simple password on your Wi-Fi network just doesn't cut it anymore. We live in a world of "Bring Your Own Device" (BYOD), which has completely erased the old boundaries between personal gadgets and the corporate network. Every single smartphone, tablet, and laptop that hops onto your Wi-Fi is a potential doorway for trouble.
This is a high-stakes game, especially in places like schools, retail stores, and offices. You're not just handing out internet access; you're the guardian of sensitive student records, private customer data, and mission-critical business files. One slip-up, one breach, and you could be facing serious financial and reputational damage. Thinking about security isn't an IT chore—it's a core business function, critical for Education, Retail, and Corporate sectors alike.
Evolving Threats Demand Smarter Solutions
The playbook for securing Wi-Fi has changed dramatically. A modern, robust security strategy means building protections in from the very beginning, not just bolting them on as an afterthought. This proactive approach is a lot like embracing 'Shift Left Security' principles in the software world.
We've come a long way from the easily cracked encryption standards of the past. While WPA2 is still common, the industry standard is now WPA3. Introduced in 2018, it brought major improvements, most notably a protocol called Simultaneous Authentication of Equals (SAE), which is far better at stopping brute-force password guessing attacks.
Today's security is about more than just a strong password. It’s about identity-based access, intelligent authentication, and complete visibility over your wireless environment.
To get you started, let's break down the layers of security we'll be discussing.
Key WiFi Security Layers at a Glance
Here's a quick overview of the essential security concepts we'll explore, from core encryption to sophisticated user authentication.
| Security Layer | Primary Function | Ideal Environment |
|---|---|---|
| WPA2/WPA3 | Encrypts traffic between devices and the access point. | All environments. WPA3 is the current standard. |
| Captive Portal | Provides a branded login page for guest access. | Hospitality, retail, public venues, Education. |
| IPSK / EasyPSK | Assigns a unique key to each user or device. | Co-working spaces, corporate BYOD, Education. |
| 802.1X / RADIUS | Authenticates users against a central directory (e.g., Azure AD). | Enterprise, Education, Healthcare. |
Each of these layers adds another level of defense, creating a comprehensive security posture for your network.
The Critical Role of Advanced Authentication
This is where things get really interesting. Instead of a one-password-fits-all approach, modern systems focus on verifying the user, not just the device they're holding. This is a fundamental shift in how we think about access control.
Here are a few key Authentication Solutions you'll encounter:
- Captive Portals: Think of the branded login page you see at a hotel or coffee shop. This is a captive portal. It acts as a controlled gateway, neatly separating public guest traffic from your secure internal network.
- Identity Pre-Shared Keys (IPSK): Also known as EasyPSK, this powerful method gives every user or device its own unique password. If an employee leaves or a tablet is lost, you simply revoke its specific key without affecting anyone else. No more changing the Wi-Fi password for the entire company!
- Enterprise-Grade Authentication: For the highest level of security, you'll want to use something like 802.1X. This protocol integrates directly with user directories (like Azure AD or Google Workspace) to ensure only verified, authorized individuals can get on the network.
Fortunately, you don't have to be a network security guru to implement these. Leading platforms from providers like Cisco and Meraki make deploying these advanced security layers surprisingly straightforward. By putting these strategies into practice, you can transform your Wi-Fi from a potential weak point into a secure, well-managed asset.
Building a Strong Foundation with WPA3 Encryption
When you're setting up or overhauling your venue's Wi-Fi, the absolute first thing to lock down is encryption. Think of it as a secret code that scrambles all the data flying through the air, making it completely unreadable to anyone trying to snoop. For a long time, WPA2 was the standard, but it's showing its age.
Today, WPA3 is the only real choice for serious wireless security. It’s a huge step up, specifically built to fend off the kind of aggressive, automated password-guessing attacks that can tear through older protocols. Moving to WPA3 isn't just a minor update; it's a non-negotiable step for building a secure network.
Why WPA3 Is a Game-Changer
What makes WPA3 so much better? It all comes down to the initial "handshake" when a device first connects. WPA3 uses a sophisticated method called Simultaneous Authentication of Equals (SAE), which is incredibly resistant to brute-force attacks.
Even if a hacker manages to capture the data packets from that initial connection, they can't take it offline and hammer it with password attempts. That was a critical flaw in WPA2. This single improvement makes a world of difference. For a deeper technical look, you can learn more about how WPA3 works in our detailed guide. This is a must-have for any business, whether you're a cafe or a corporate office with a BYOD policy.
Moving from WPA2 to WPA3 is like swapping a basic door lock for a high-security vault door. It fundamentally changes the level of difficulty for an attacker trying to get in.
Beyond Encryption: Creating Digital Boundaries
While tough encryption is your first line of defense, it shouldn't be your only one. A truly secure network needs digital walls to separate different users and devices. The most straightforward way to do this is with separate Service Set Identifiers (SSIDs)—that’s just the technical term for the Wi-Fi network names people see on their devices.
You wouldn't hand a visitor a master key to your entire building, would you? The same logic applies here. By creating distinct networks for different groups, you can contain potential threats and strictly control who can access what.
Practical SSID Segregation Strategies
So, what does this look like in practice? A well-designed network will have several SSIDs, each with its own specific job and security rules.
Here are a few common examples:
- Guest Network: This is your public-facing Wi-Fi. It needs to be completely isolated from your internal operations and should use a Captive Portal for users to log in. We'll get into those in the next section.
- Corporate Staff Network: This is for employees' personal devices under your BYOD policy. You can secure this with smart Authentication Solutions like IPSK (sometimes called EasyPSK), which gives each employee a unique key for their devices.
- Internal Operations Network: This is the high-security zone. It's for company-owned devices and critical systems like POS terminals in Retail or internal servers. Access should be tightly restricted, probably using enterprise-grade authentication.
- IoT Device Network: Got smart thermostats, security cameras, or other connected gadgets? They absolutely need their own isolated network. This prevents a vulnerability in a smart lightbulb from compromising your entire business.
This segmented approach is a core principle of modern network security. Leading hardware from providers like Cisco and platforms like Meraki make setting up and managing these separate networks surprisingly simple.
By combining the ironclad encryption of WPA3 with smart SSID segregation, you create a layered, resilient defense that protects your data, your staff, and your customers from the ground up.
Creating Secure Guest Access with Captive Portals
Offering guest Wi-Fi is practically a necessity these days, whether you're running a coffee shop, a busy corporate office, or a sprawling university campus. But let’s be real—it can also open up a can of worms from a security perspective. This is precisely where a Captive Portal proves its worth.
A Captive Portal is that branded login page everyone sees before they can hop onto your guest network. It’s more than just a gatekeeper; it's a clean, professional entry point. This is your chance to lay out your terms of service, maybe share a special offer, and, most importantly, control who gets onto your network.
From Security Risk to Brand Opportunity
Without a portal, your guest network is the wild west. With one, you create a controlled, secure environment. The security needs can vary dramatically depending on where you are:
- Education: In a university library, you have to ensure every student's connection is private and secure from their peers, which is a perfect use case for a Captive Portal.
- Retail: For a boutique or cafe, the goal is simple access, but you still need to protect your business network and other shoppers from potential threats.
- Corporate BYOD: When visitors bring their own devices into your lobby, you absolutely must ensure they can't get a glimpse of your sensitive internal network.
Modern systems, like those from Cisco Meraki, have made setting up these portals incredibly straightforward. You can customize the page with your own branding, turning what is essentially a security checkpoint into a positive, welcoming experience for your guests. To dig deeper, you can explore the benefits of a Wi-Fi Captive Portal in our detailed guide.
The Power of Client Isolation
One of the most critical security features for any guest network is client isolation. The concept is simple but incredibly powerful: it stops devices connected to the guest Wi-Fi from seeing or talking to each other.
Think of it as giving each user their own private, invisible tunnel to the internet. Someone in a hotel lobby can’t snoop around and find another guest's laptop. This one setting dramatically cuts down the risk of malware spreading between devices and protects your visitors from one another.
Client isolation isn't just a nice-to-have feature; it's a fundamental requirement for any responsible guest Wi-Fi deployment. It's the digital equivalent of giving every visitor their own private, locked room.
This is especially important when you consider how wary people are of public networks. A recent survey showed that nearly 40% of Americans believe they've had a security issue, like data theft, after using public Wi-Fi. Despite this, many don't take precautions, which makes built-in security like client isolation non-negotiable. You can read the full research on public Wi-Fi safety to get a better sense of user habits.
Smarter Authentication Solutions for Guests
Your Captive Portal is also the perfect place to roll out more intelligent Authentication Solutions. Forget about that single, shared password written on a whiteboard that never gets changed. It's time to use methods that are both more secure and easier to manage.
- Social Logins: Let users connect with their existing social media or email accounts. It's a smooth, frictionless experience for them and, with their consent, can provide you with useful demographic insights.
- Voucher Systems: Perfect for hotels or paid-access hotspots. You can generate unique, time-limited access codes for each guest, giving you complete control.
- IPSK and EasyPSK: For trusted partners or longer-term guests in a BYOD setting, an Identity Pre-Shared Key (IPSK, also called EasyPSK) is a great option. It assigns a personal, unique password that can be easily revoked when they leave, without affecting anyone else.
By combining a branded Captive Portal with strong client isolation and modern authentication, you transform a potential vulnerability into a secure, managed, and valuable asset. It shows your guests you take their digital safety seriously while protecting your own critical network infrastructure.
Moving Beyond a Single Shared Password
Let's be honest: relying on one password for every user and every device is a huge security gamble. In any modern setting—a bustling school campus, a retail shop, or an office with a bring-your-own-device (BYOD) policy—that one password is your weakest link. If it gets out, your entire network is wide open.
This is exactly why the conversation around securing Wi-Fi has evolved. It's no longer just about passwords; it's about smart, identity-based authentication. The idea is to grant access based on who is connecting, not just what password they managed to find scribbled on a whiteboard. This approach gives you far more granular control, beefs up your security, and makes your life as an administrator a whole lot easier.
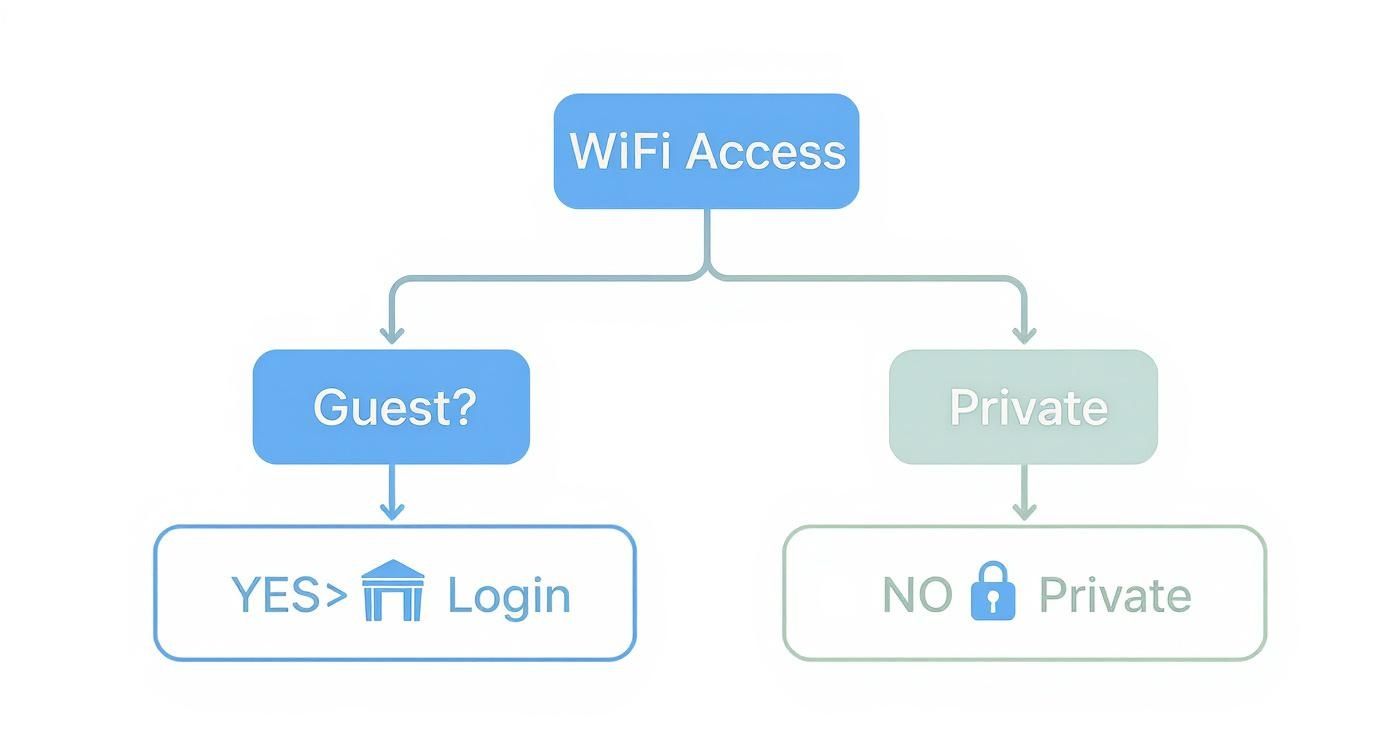
This simple flowchart lays out the first critical decision: is the user a temporary guest or a trusted member of your team?
As you can see, the path splits immediately. Guests are directed to a login portal, while trusted users are routed to a more secure, private network. This is the foundation of a layered security strategy.
Introducing Individual Keys With IPSK and EasyPSK
Think about this real-world scenario in a school. A student loses their tablet. With a single shared password, you have no choice but to change the password for the entire campus and then painstakingly update every single device. It's a logistical nightmare.
This is where Identity Pre-Shared Key (IPSK)—often called EasyPSK—changes the game.
With IPSK, you generate a unique, individual password for each user or device. Now, when that student’s tablet goes missing, you just log into your management dashboard (like the one from Cisco Meraki) and revoke that one specific key. Problem solved in seconds, and no one else is affected.
This method is just as powerful in a corporate BYOD environment. You can issue keys to new employees for their personal devices, and when they leave the company, their access is instantly cut off. It's a massive leap forward in both security and day-to-day efficiency.
Enterprise-Grade Security With 802.1X and RADIUS
For organizations that can't compromise on security, the gold standard is 802.1X paired with a RADIUS server. It might sound complex, but the concept is actually pretty straightforward. Instead of storing passwords on the access points themselves, 802.1X checks a user's credentials against a central directory.
What does that mean in practice? You can use your existing employee or student logins from services like Microsoft Azure AD or Google Workspace to grant Wi-Fi access. An employee’s network privileges are tied directly to their corporate account. If their main account is disabled, their Wi-Fi access vanishes right along with it.
Adopting 802.1X is like hardwiring your Wi-Fi security directly into your organization's central identity system. It creates a single source of truth for user access, which is incredibly powerful for large-scale deployments in corporate, healthcare, or educational environments.
This approach gives you unmatched control and visibility. For a more technical look, our guide offers a deep dive into the mechanics of 802.1X authentication. It's the ultimate solution when security and compliance are non-negotiable.
Comparing Modern WiFi Authentication Methods
Picking the right authentication method really comes down to your specific needs. What works for guest convenience in a hotel lobby won't cut it for a corporate headquarters handling sensitive data. This table offers a side-by-side look at different authentication methods to help you select the right level of security for your users.
| Authentication Method | How It Works | Best For | Security Level |
|---|---|---|---|
| Captive Portal | Users log in via a branded web page. | Guest access in Retail, Education, and public venues. | Good |
| IPSK / EasyPSK | Each user or device gets a unique password. | Corporate BYOD, student housing, co-working spaces. | Better |
| 802.1X / RADIUS | Users authenticate with directory credentials (e.g., Azure AD). | Enterprise corporate networks, Education, healthcare. | Best |
At the end of the day, moving beyond a single shared password isn't just a best practice; it's a fundamental requirement for securing any modern Wi-Fi network. By implementing identity-based solutions like IPSK or 802.1X, you're building a network that is not only far more secure but also much simpler to manage.
Keep a Watchful Eye: Proactive Monitoring and Threat Defense
Securing your Wi-Fi isn't a "set it and forget it" task. It's an active, ongoing process that demands constant attention. New threats emerge constantly, so your mindset has to shift from a one-time setup to a continuous, proactive defense.
This means staying vigilant. A huge part of this is keeping all your network hardware—your access points, switches, and routers—religiously up to date. Firmware updates aren't just for adding flashy new features; they often contain critical security patches that close loopholes discovered by security researchers.
The Non-Negotiable Need for Firmware Updates
Think of firmware as the operating system for your network gear. When a manufacturer finds a vulnerability, they release a patch. Delaying that update is like leaving your front door unlocked after hearing about a string of break-ins down the street. It’s essential to stay on top of hardware risks, like addressing critical security vulnerabilities in devices, to maintain a strong defense.
Thankfully, modern platforms make this much easier. Cloud-managed solutions, like those from Cisco Meraki, can automate firmware updates entirely. This ensures your infrastructure is always running the latest, most secure version without you having to manually touch every single device.
Your network is only as strong as its most outdated piece of equipment. Regular, timely firmware updates are one of the simplest and most effective ways to bolster your defenses against emerging threats.
What’s Happening on Your Network?
Beyond updates, you need visibility. Network monitoring and logging are your eyes and ears, giving you a clear picture of what’s happening on your wireless network at all times. Who is connecting? When are they connecting? What are they trying to access?
By establishing a baseline of normal activity, you’ll quickly spot anomalies that could signal an attack. A sudden spike in failed login attempts on your Captive Portal, for instance, could be a brute-force attack in progress. If a guest device suddenly starts probing sensitive internal servers, you’ll know something is very wrong. Diving into network monitoring best practices can give you a solid foundation here.
Your 24/7 Digital Security Guard
To truly elevate your defense, you need a system that can actively fight back. That’s where a Wireless Intrusion Prevention System (WIPS) comes in. A WIPS is like a dedicated, 24/7 security guard for your airspace, constantly scanning for wireless threats.
This isn't just passive observation. A WIPS can automatically detect and neutralize threats in real time.
- Rogue Access Points: It spots unauthorized APs that an employee or attacker might plug into your network to create a backdoor.
- "Evil Twin" Attacks: It identifies malicious hotspots that mimic your legitimate network name, tricking users into connecting so their credentials can be stolen.
- Denial-of-Service (DoS) Attacks: It detects and mitigates attempts to flood your network with traffic to bring it down.
This proactive stance is absolutely vital for protecting the sensitive data often handled in education, retail, and corporate BYOD environments.
With the number of IoT devices expected to hit nearly 39 billion by 2030, the potential attack surface of any Wi-Fi network is exploding. This makes continuous monitoring essential to counter the rising costs of cybercrime, which are projected to reach $10.5 trillion globally by 2025. Combining regular updates, vigilant monitoring, and an active WIPS builds a resilient defense that can stand up to modern challenges.
Answering Your Top Wi-Fi Security Questions
As you start planning your network security, you're bound to run into some questions. It’s a field full of acronyms and concepts that aren't always straightforward. To help cut through the noise, I've put together answers to the questions we hear most often from people running networks in education, retail, and offices with heavy BYOD use.
What's the Single Most Important Step for Business Wi-Fi Security?
If you do only one thing, get rid of the single, shared password for your staff and internal networks. This is, without a doubt, the biggest vulnerability most organizations have. One password that everyone knows is just asking for trouble.
The real game-changer is switching to an identity-based authentication solution. For your internal team, this means looking at technologies like Identity Pre-Shared Keys (IPSK) or, for even stronger security, the 802.1X standard. Both of these approaches tie network access to a specific person or device, which gives you immediate control and a clear audit trail. When a single compromised password can no longer bring down your entire network, you've already made a massive security improvement.
The biggest security win comes from moving away from a shared secret and toward individual accountability. When you can grant and revoke access on a per-user basis, you fundamentally change your security posture for the better.
How Is IPSK Better Than a Regular Wi-Fi Password for BYOD?
A standard Wi-Fi password is like having one master key for your entire building. If an employee leaves, you have to change the lock and then go around and give the new key to everyone—a huge pain that means reconfiguring every single device.
Identity Pre-Shared Key (IPSK), sometimes called EasyPSK, is completely different. It lets you generate a unique, personal password for each user or even each device. This is a perfect solution for BYOD environments. You can give an employee's phone its own key and their laptop a separate one.
When that person leaves the company, you just deactivate their specific keys. Nobody else is affected, and the change is instant. It's this granular level of control that makes IPSK a far more practical and secure way to manage a network with lots of personal devices.
Can I Use a Captive Portal for Marketing in My Retail Store?
Absolutely! This is one of the best parts about modern Captive Portal systems, especially those designed to integrate with platforms like Cisco Meraki. You can transform your login page from a simple utility into a genuine marketing and customer engagement tool.
Think about it: a customer connects to your Wi-Fi, and instead of a boring password box, they see your branding, a flash sale for that day, or an invite to your loyalty program.
You can use these portals to:
- Display Promotions: Announce a "deal of the day" or new product arrivals right on the login screen.
- Build Your Mailing List: Offer free Wi-Fi in exchange for an email address (with their full consent, of course).
- Drive Social Engagement: Add links to your Instagram or Facebook pages.
Suddenly, your guest Wi-Fi isn't just a cost—it becomes a strategic asset that helps you connect with customers and drive sales.
Is WPA3 Still Necessary if I Use 802.1X Authentication?
Yes, it is, and it's a critical point to understand. WPA3 and 802.1X aren't an either/or choice; they work together to create layers of security, each protecting the network in a different way.
Here’s a good analogy: 802.1X is the high-tech security guard at the front door. It’s in charge of authentication—checking IDs and making sure only authorized people are allowed inside the building.
WPA3, on the other hand, is the privacy shield that protects all the conversations happening inside the building. It handles the encryption, scrambling all the data that flows between a user's device and the access point after they've been authenticated. This stops anyone from eavesdropping on their traffic. WPA3 also adds crucial protection against offline password-cracking attacks, a major weakness of older protocols.
When you combine the robust identity verification of 802.1X with the powerful data encryption of WPA3, you get the gold standard for wireless security. This setup is ideal for any corporate or education setting where protecting sensitive information is a top priority.
What Is SSID Hiding and Does It Actually Improve Security?
SSID hiding is a feature on your router that stops it from broadcasting your network’s name. The theory is that if attackers can’t see the network, they can’t attack it. In practice, this offers almost no real security benefit.
While hiding your SSID might keep a casual neighbor from seeing your network listed, anyone with basic, freely available scanning tools can find a "hidden" network in seconds. Relying on it gives you a false sense of security.
You’re much better off spending your time and effort on security measures that actually work. Focus on implementing WPA3 encryption, using strong authentication solutions like IPSK or 802.1X, and properly segmenting your network with VLANs. These are the foundational steps that provide real, measurable protection. SSID hiding is more security theater than an effective defense.
Ready to implement these advanced security strategies and provide a world-class Wi-Fi experience? The team at Splash Access specializes in deploying powerful, user-friendly guest Wi-Fi solutions on Cisco Meraki hardware. Learn more about how we can help secure your network today.