Ever wondered what secretly holds your entire digital world together? Let's chat about the backbone of a network. Think of it as the superhighway system for all your data, linking together different parts of your local network, your Wi-Fi access points, and all your devices, while also connecting them to the wider internet. It's the unsung hero of great Wi-Fi!
Why Your Network Backbone Is Its Most Critical Component
Let’s get friendly with an analogy. Picture your business as a sprawling, bustling city. The network backbone is the system of major highways, tunnels, and bridges that lets traffic move freely and quickly between different districts. If those main arteries are narrow, full of potholes, or poorly planned, the entire city grinds to a halt.
That's exactly what happens with a weak network backbone. It's the high-capacity, high-speed infrastructure that makes sure data gets where it needs to go without annoying delays.
This core system is the foundation for any modern digital experience. It's what supports everything from a simple social Wi-Fi login at a coffee shop to complex security setups in a large corporate office. Without a solid backbone, even the most powerful Cisco Meraki access points can't deliver the awesome performance they're capable of.
Powering Modern Wi-Fi Experiences
In places like schools, retail stores, and corporate offices, the Wi-Fi network is under constant pressure. A powerful backbone is what makes today’s essential features work flawlessly:
- Seamless Captive Portals: It makes sure that branded login pages pop up instantly. When you offer guest wifi, that first impression is everything, and a slick Captive Portal makes you look like a pro.
- Secure Authentication: It reliably manages advanced security protocols like IPSK and EasyPSK. These are superstar Authentication Solutions for keeping different types of traffic separate and protecting data, especially in busy "bring-your-own-device" (BYOD Corporate) environments.
- Consistent Performance: It acts like a traffic cop, preventing bottlenecks and making sure every single user—whether they're a student in an Education setting, a shopper in Retail, or an employee—gets a fast, stable connection.
A weak backbone is a recipe for disaster. It leads to frustratingly slow logins, dropped connections, and gaping security holes. Investing in this core infrastructure isn't just a good idea; it's the first and most important step in building a network that can actually handle today's demands.
The Building Blocks of a Strong Backbone
Before diving deeper, it helps to know the key players that make up a network backbone. Here’s a quick, friendly breakdown of the core components and what they do.
| Key Components of a Network Backbone |
| :— | :— | :— |
| Component | Role in the Backbone | Simple Analogy |
| Core Switches & Routers | High-performance devices from brands like Cisco that direct traffic at the very center of the network. | The central station or major highway interchange of your network. |
| High-Speed Cabling | Typically fiber optic cables that physically transmit data at incredible speeds. | The multi-lane superhighways connecting different parts of the city. |
| Distribution Switches | Aggregate traffic from smaller networks (like different floors or buildings) and connect it to the core. | The major on-ramps and off-ramps that feed traffic onto the main highway. |
| Network Management System | Software, like the Meraki dashboard, used to monitor, manage, and secure the entire backbone. | The city's traffic control center, watching over everything to keep it running smoothly. |
Understanding these pieces helps you see how they all work together to create a reliable and fast network. It's not just about one piece of hardware, but how the entire system is designed.
The physical hardware, often high-speed fiber optic cables, forms the literal data highways. To truly grasp why a powerful backbone is non-negotiable, it’s worth looking at the tech itself. You can learn about the 10 key benefits of fiber optic internet to see how that raw speed at the core translates into a better experience for every single device.
Ultimately, building a powerful and dependable digital presence starts by strengthening this essential foundation. You can find more practical advice on this in our guide to building a more resilient network. A well-designed backbone is the unsung hero that guarantees a smooth and secure digital journey for everyone who connects.
The Two Layers of a Network Backbone
When we talk about the backbone of a network, it’s easy to just picture a server room humming with equipment. While that’s certainly part of the story, a truly effective backbone operates on two distinct layers that have to work together perfectly.
Think of it like building a world-class transit system. You absolutely need the physical tracks and powerful trains, but you also need the smart signaling system that tells everything where to go, preventing collisions and keeping things running on time.
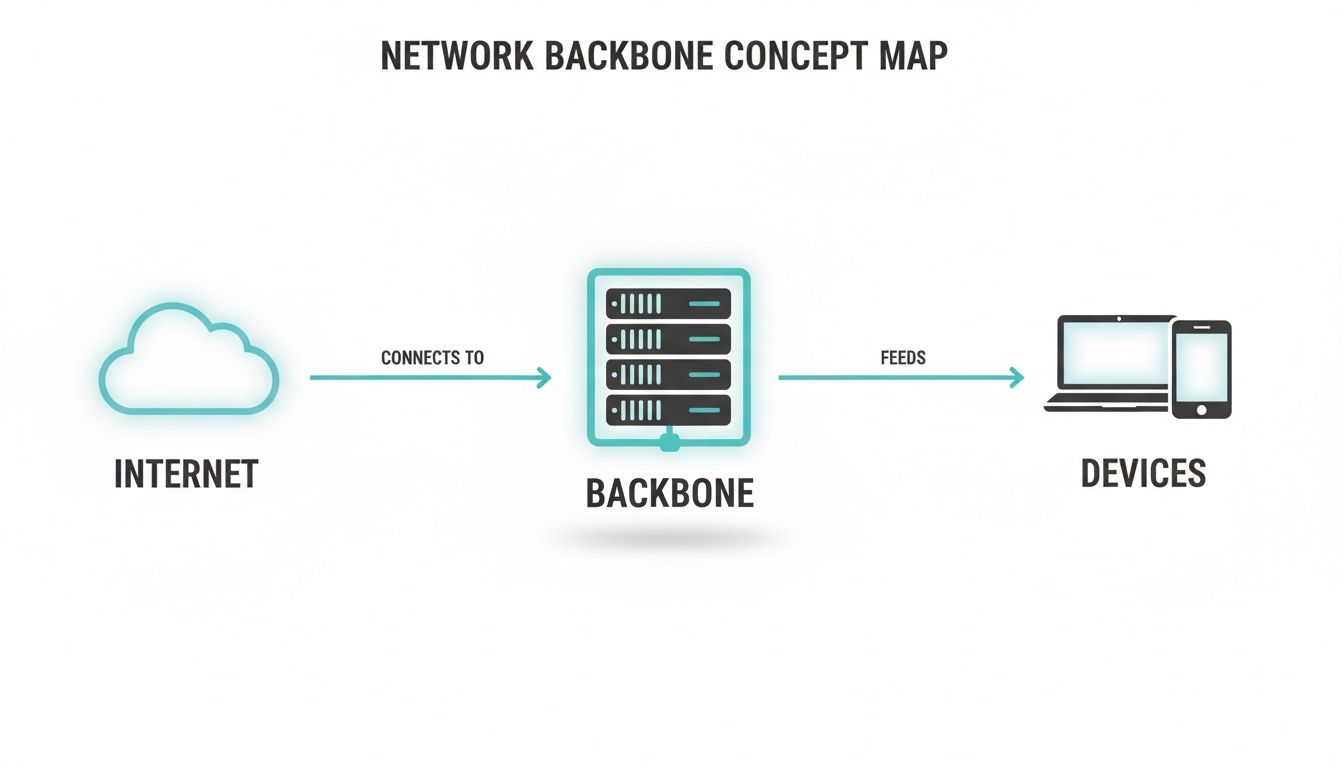
This diagram shows how data flows from the internet, through the network backbone, and finally to the end-user devices.
You can see how the backbone acts as the critical bridge between the wider internet and all the local devices that need to connect. It’s the central nervous system.
The Physical Backbone: Your Hardware Foundation
First up is the physical layer. This is all the tangible hardware you can actually see and touch—the real-world steel and silicon that forms your network’s superhighway. It’s the collection of high-speed fiber optic cables, powerful core switches, and high-performance routers that shuttle data packets around at incredible speeds.
For any modern business, this means investing in hardware that can take a beating. Equipment from providers like Cisco and Cisco Meraki is built specifically for this role, acting as the heavy-duty engines of your data transport system. A robust physical backbone isn't just nice to have; it's the non-negotiable first step to ensuring your network can handle today's intense traffic demands. Without it, everything else just grinds to a halt.
The Logical Backbone: Your Smart Traffic Management
The second layer is the logical backbone. This isn't about hardware. It’s the intelligent design and organization—the set of rules—that governs how data moves across that physical hardware. It’s what creates order out of the potential chaos of constant data flow.
A huge part of this is creating Virtual LANs (VLANs). Imagine your physical network highway has multiple, completely separate lanes. The logical backbone is what designates these lanes for specific kinds of traffic.
- Lane 1 (Express Lane): For critical internal business operations.
- Lane 2 (Guest Lane): For public guest wifi traffic, totally isolated from internal systems.
- Lane 3 (BYOD Lane): For employee-owned devices in a BYOD Corporate setting.
This segmentation is absolutely crucial for both security and performance. If you want to dive deeper into how these segments fit into a larger plan, our guide to understanding network topology in a computer provides a great overview.
This logical separation is what ensures that a guest using social login on a captive portal in a Retail store cannot accidentally access the company's private financial data. It keeps all the different types of traffic neatly organized and secure, which is essential for any modern network.
How the Two Layers Support Modern Authentication
This is where the magic really happens, especially when it comes to security. Advanced authentication solutions like IPSK (Individual Pre-Shared Key) or EasyPSK depend completely on both the physical and logical layers working in harmony.
Think about an Education environment. A university might use an IPSK system to give each student a unique Wi-Fi key. The physical Meraki backbone provides the raw horsepower and speed to handle thousands of simultaneous connections. At the same time, the logical backbone uses VLANs to ensure each student's traffic is walled off in its own secure tunnel.
This means one student can't see another's device on the network, even though they're connected to the same Wi-Fi. It’s a powerful combination that delivers a seamless user experience and ironclad security. This two-layered approach is the secret to building a network backbone that is not only fast but also incredibly secure and adaptable to any need, from a simple social wifi hotspot to a complex corporate infrastructure.
Designing a Backbone for Performance and Reliability
If the backbone of a network goes down, it can bring an entire organization to a grinding halt. Yikes! That's why any intelligent design boils down to two critical goals: making it bulletproof and making it blazing fast. Let's break down the practical ways to build a network core that can handle intense demand and shrug off failures without breaking a sweat.
The first pillar of a strong backbone is redundancy. Think of it like your car’s GPS. If a major road is suddenly closed, it instantly reroutes you down a different path to keep you moving. A redundant network backbone does the exact same thing for your data, creating backup paths so that if one connection fails, traffic instantly finds another way to its destination.
This principle is absolutely essential in places where downtime just isn't an option, like a busy Retail store during a holiday sale or a university campus during finals week.
Building Resilience with Failover Configurations
To get that level of reliability, network engineers use failover configurations built with high-quality gear like Cisco Meraki switches and routers. This really just means having duplicate hardware and links ready to take over at a moment's notice.
A few common approaches include:
- Multiple Core Switches: Instead of putting all your trust in a single core switch, a redundant design uses two or more. If the main one fails, the secondary switch immediately takes over all traffic-directing duties.
- Diverse Physical Paths: This means running critical fiber cables through completely different physical routes or conduits. It’s a simple but effective way to protect against accidental damage—like a construction crew cutting a cable—that could otherwise take the whole network offline.
- Link Aggregation: This technique involves bundling multiple physical connections into a single, more powerful logical link. It not only boosts your total available bandwidth but also means that if one cable in the bundle fails, the others keep the connection alive.
A well-designed backbone with proper redundancy ensures that a single point of failure won't cause a catastrophe. This level of planning is what separates a fragile network from a truly resilient one, keeping your business online and productive.
For any organization planning a major overhaul, like a data center move, a well-thought-out backbone is crucial for navigating the process without major disruptions. This helpful data center migration checklist highlights the importance of this foundational work. Building that redundancy in from the start makes these big projects go a lot smoother.
Designing for Peak Performance Demands
Resilience is only half the battle; your backbone also has to be incredibly fast. In modern BYOD Corporate environments, the network is constantly flooded with high-bandwidth traffic from video calls, cloud apps, and huge file transfers. An underpowered backbone quickly becomes a bottleneck, leading to lag, a terrible user experience, and lost productivity.
To design for peak performance, you have to anticipate your maximum traffic load and build a core that can handle it with plenty of room to spare. This involves using powerful core switches capable of routing billions of bits of data per second. Managed switches are a game-changer here, giving administrators fine-grained control over how traffic flows. You can get a deeper dive into what managed switches are in our detailed guide.
A high-performance backbone ensures that the systems people interact with directly, like captive portals for guest wifi, load instantly. It also provides the speed needed for authentication solutions like IPSK and EasyPSK to work flawlessly, creating a smooth and secure connection for every user.
As organizations grow, their data demands skyrocket. The global Backbone Network Services market was valued at about USD 106.9 billion in 2025 and is projected to hit approximately USD 176.2 billion by 2032. This trend shows just how critical powerful and reliable network infrastructure is becoming.
Securing Your Core Network Infrastructure
It's a huge mistake to think of your network backbone as just a highway for data. An insecure backbone is the same as leaving the front door of your entire organization unlocked. Real, effective network security starts right at this core level—long before a user ever even thinks about typing in a Wi-Fi password. Let's talk about the essential steps to protect your network’s very foundation.
Protecting this core isn't just about stopping outside attacks; it's about creating controlled, secure zones inside your network. This is where powerful Cisco Meraki equipment really shines. By building robust security measures directly into your core switches and routers, you create a network that is secure by its very design.
This kind of solid foundation is what makes modern guest Wi-Fi possible. It allows you to offer seamless access through a captive portal without ever putting your internal systems at risk.
Building Your Digital Fortress with Cisco Meraki
At the heart of any secure backbone, you'll find three fundamental tools: firewalls, access control lists (ACLs), and network segmentation. When you get these configured on your core Cisco gear, they work in concert to create a formidable defense against unauthorized access and potential data breaches.
- Firewalls: These are the primary guards at your network's entrance. They inspect all incoming and outgoing traffic, blocking anything that looks suspicious or violates the security rules you've set.
- Access Control Lists (ACLs): Think of ACLs as highly specific security checkpoints within your network. They enforce rules that decide which users or devices can get to certain areas, preventing—for example—a guest on your social wifi from ever reaching sensitive company servers.
- Network Segmentation (VLANs): This is the crucial practice of splitting your network into smaller, isolated virtual LANs. By creating separate VLANs for corporate devices, guest access, and BYOD traffic, you guarantee that a security problem in one segment can't spread to the others.
For organizations in Education or BYOD Corporate environments, where countless personal devices connect every day, these measures aren't just a good idea—they're absolutely essential. Without them, you're creating a massive attack surface that puts sensitive student or company data in jeopardy.
A secure backbone isn't an afterthought; it's the bedrock of trust. From the moment a user connects, whether via a social login or a complex corporate credential, your security policies must already be in place and actively enforced by the core infrastructure.
The Linchpin for Advanced Authentication Solutions
This is where a secure backbone truly proves its worth. It acts as the critical enabler for sophisticated authentication solutions like IPSK (Individual Pre-Shared Key) and EasyPSK. These methods go way beyond a single shared password by assigning a unique, private key to every single user or device.
Picture a busy Retail environment. With an IPSK system running on a secure backbone, the point-of-sale terminals, staff tablets, and the public guest wifi are all completely isolated from one another. Each device has its own key and is confined to its specific network segment, making it nearly impossible for an unauthorized user to move laterally across the network. Our detailed guide on network security infrastructure explains how these layers of protection work together to create a truly secure environment.
This level of granular control is only possible when the backbone is properly set up to enforce these policies. It ensures that from the very first interaction at the captive portal, each connection is treated as a unique, secure session. This is the modern standard for delivering safe, reliable connectivity in any environment where data security is a top priority.
Putting the Backbone to Work: Real-World Scenarios
The true value of a network backbone isn't in the cables and switches themselves, but in what they empower. Let's look at how a well-designed core network becomes the unsung hero, quietly enabling seamless and secure connectivity in a few different environments.
Picture a busy retail store on a weekend. Shoppers are jumping onto the guest wifi through a branded captive portal, maybe using a quick social login. At the same time, cash registers are processing credit card payments, and staff are using handheld scanners to update inventory. A solid backbone, likely built on dependable Cisco hardware, juggles all this traffic effortlessly, keeping both customers happy and business operations running smoothly.
Securing the Modern Campus in Education
Now, let's head over to a sprawling university campus. Here, the backbone of a network is the central nervous system for thousands of students and faculty. It's a massive BYOD (Bring Your Own Device) free-for-all, where everyone needs reliable access to digital libraries, video lectures, and online collaboration platforms from their own devices.
This is where robust authentication solutions are critical. A powerful backbone gives the IT department the muscle to deploy systems like IPSK or EasyPSK, which can assign a unique security key to every single student. This approach, running on hardware like Meraki access points, effectively gives each user their own private lane on the network, preventing their devices from seeing or interfering with others.
For an Education institution, the backbone is more than just an internet pipe. It’s the foundation for a secure and equitable learning environment, ensuring every student gets the access they need without putting the university's data at risk.
Achieving this kind of tight security and network segmentation is only possible with a backbone that can handle the complex routing and policy enforcement needed in such a dense environment. It's what keeps student traffic flowing freely while walling off the sensitive administrative network from any potential threats.
Driving Productivity in the Corporate World
Finally, think about a modern BYOD Corporate office. Employees rely on instant, stable connections to cloud apps, video calls, and internal servers to get their work done. But the office also has a steady stream of clients and visitors who need a simple, secure way to get online via the guest wifi.
A capable backbone is what makes this dual-purpose network possible. It separates these two worlds completely. Employees get the high-speed, low-latency performance they need, while visitors are funneled through a branded captive portal that keeps them entirely off the internal corporate network. They can log in with a social wifi account or fill out a quick form and get online without posing a security risk.
The backbone is the silent workhorse that delivers on key promises:
- No More Slowdowns: Employees can collaborate on huge files or join bandwidth-heavy video conferences without a hiccup.
- Ironclad Security: Guest traffic is completely isolated from the internal network, closing a common and significant security hole.
- A Polished Guest Experience: The captive portal loads instantly, reinforcing the company's professional brand from the first click.
The pressure on these networks is only growing. By 2025, mobile broadband networks are projected to cover about 96% of the world’s population, which means more and more traffic is being offloaded onto local Wi-Fi. This trend forces every venue to plan for huge spikes in demand from things like video streaming and cloud backups. As detailed in this report on the state of mobile internet coverage, these global shifts make a strong local backbone more critical than ever.
In the end, no matter the industry, the backbone of a network is what allows an organization to build customized, secure, and high-performing digital experiences for everyone who walks through its doors.
Your Local Network's Gateway to the World
Think of your local network backbone as the ultimate on-ramp. It's a powerful, high-speed system, but its real job is to connect your business to the vast global superhighway that is the internet. This global backbone is a mind-boggling web of undersea fiber optic cables and continent-spanning data centers that house all the cloud services we rely on.
This is what allows a student on campus Wi-Fi in Education to pull data from a research server halfway across the globe in an instant. It’s the magic that lets a shopper in a Retail store use a social login on the guest wifi, connecting their phone to servers thousands of miles away without a second thought.
From Your Office to the Cloud
For businesses running on cloud-managed platforms like Cisco Meraki, this connection is everything. The entire Meraki dashboard—the control panel for your whole network—lives in the cloud. That means the performance of your management tools and all your user-facing services, like Captive Portals and Authentication Solutions, is completely dependent on the quality of that link from your local network to those global data centers.
Even with the best hardware on-site, a sluggish or flaky connection to the global backbone will cause problems. This is exactly why a solid local backbone of a network is non-negotiable; it creates a clean, fast, and stable pathway for all your data to travel out to the rest of the world and back again.
The Undersea Superhighway
It’s easy to picture the internet as an invisible cloud, but it has a very real, physical foundation. An incredible 99% of all international data travels through submarine fiber-optic cables crisscrossing the ocean floor. These cables are the true physical backbone powering virtually every cloud service and international connection we use daily.
You can dive deeper into this global infrastructure and its impact in the Global Connectivity Report 2025. For any business offering guest wifi, this underscores a critical point: your user's experience depends just as much on these massive, long-haul links as it does on your own equipment.
When someone in a BYOD Corporate setting authenticates using IPSK or EasyPSK, their request zips through your local Cisco core switch, out to the internet, hits a cloud authentication server, and gets a response—all in a fraction of a second. This incredible journey shows just how vital your local backbone is as that first and last mile.
All this global traffic is directed by sophisticated routing protocols that are constantly finding the most efficient path for data to take. To see how this complex routing works within a cloud-managed network, our guide on BGP the Meraki Way breaks down how intelligent, global-scale routing is essential for delivering a world-class digital experience.
Got Questions? We've Got Answers
Let's tackle some of the most common questions people have about the backbone of a network. Getting this right is critical, as it directly shapes your Wi-Fi performance, security, and the kind of experience you can offer.
How Does a Network Backbone Affect My Guest Wi-Fi Speed?
Your guest Wi-Fi is only as fast as its slowest component, and very often, that's the network backbone. You can have the best Cisco Meraki access points in the world, but if your core infrastructure is choking on the traffic from all your users, everything will grind to a halt.
Think of it like a highway. A powerful backbone is a wide, multi-lane superhighway that keeps traffic flowing smoothly, even during peak hours. This prevents those frustrating digital traffic jams when dozens of people are streaming, browsing, or using a social login on your captive portal all at once.
Can I Upgrade My Existing Backbone for Better Performance?
Absolutely. In fact, upgrading your backbone is often the single most impactful thing you can do to improve your entire network's performance. This could mean swapping out older core switches for newer, high-capacity Cisco models or simply increasing the bandwidth of your main internet connection.
For places with a lot of people, like schools in Education or busy malls in Retail, a network assessment can pinpoint exactly where the slowdowns are. This allows you to make targeted upgrades that can handle the demands of a modern BYOD Corporate environment, where everyone is connecting their own devices.
Why Is a Strong Backbone Crucial for Authentication?
Modern authentication solutions like IPSK and EasyPSK simply won't work without a solid backbone to support them. These security methods are designed to give each user their own private, secure connection by isolating their traffic from everyone else's, even on the same Wi-Fi network.
This isolation is handled at the backbone level using VLANs (Virtual LANs). A capable backbone has the muscle to enforce these security policies without breaking a sweat, ensuring that someone on the guest social Wi-Fi can never see or access devices on your internal corporate network.
Without that foundational strength, these advanced security features are just promises that can't be kept. It's the backbone that truly enables a secure, multi-layered network for both staff and visitors.
Ready to build a world-class guest Wi-Fi experience on a rock-solid foundation? Splash Access provides the powerful captive portal and authentication solutions you need to make the most of your Cisco Meraki network. Explore our features and see how we can help at the official Splash Access website.