Ever walked into a large university, a busy retail store, or your corporate office and wondered how they keep their Wi-Fi secure with thousands of different people connecting their own devices? It’s not magic, but it’s close! The secret weapon is a powerful standard called 802.1X authentication.
Think of it as a smart, digital bouncer for your network. Instead of a single password that everyone shares (and inevitably leaks), 802.1X is like a friendly but firm security guard who checks the ID of every single device before letting it in. This ensures only the right people and devices get access.
So, What Exactly Is 802.1X Authentication?
At its heart, 802.1X is an official standard that provides port-based network access control. That's a bit of a mouthful, but it basically means it acts as a gatekeeper for both your wired and wireless connections. It ditches the old-school, shared password model in favor of a much smarter system where every user or device has to prove its identity with unique credentials.
This individual verification is precisely what makes it the gold standard for network security, especially in today's world. It's the invisible force protecting payment systems in a bustling Retail environment, managing countless student connections on a sprawling campus in the Education sector, and securely separating employee-owned devices in a corporate BYOD setting.
Why It Matters More Than Ever
In the not-so-distant past, network access was much simpler. But with the explosion of personal devices (hello, BYOD!), the old "one password for everyone" approach has become a massive security hole. If just one person leaks that password, your entire network is wide open. Yikes!
802.1X flips the script by tying access to individual identity, not a shared secret. This brings some huge advantages:
- Supercharged Security: It goes way beyond basic passwords, often using digital certificates or unique keys that are tied to a specific device.
- Granular Control: IT admins gain the power to create detailed access rules. They can decide who connects, what they can access, and even which devices are allowed on the network.
- Clear Visibility: Since every connection is linked to a user or device, you get a crystal-clear audit trail. This is a game-changer for troubleshooting and meeting compliance standards.
The Modern, User-Friendly Approach to Network Security
Today’s modern authentication solutions have built on the 802.1X foundation with clever methods like Identity Pre-Shared Keys (IPSK), sometimes known as EasyPSK. Instead of wrestling with complex certificate deployments, IPSK gives each device its own unique Wi-Fi key. This makes it incredibly simple to get devices connected and manage their access, especially on networks powered by awesome hardware from Cisco and Meraki.
For the end-user, the experience is completely seamless. They might log in just once via a branded Captive Portal, and from that point on, their device is trusted and securely connected every time. It’s a world away from the annoying, repetitive login screens of the past. Adopting these updated methods is one of the smartest moves you can make, a topic we cover more in our guide on the best practices for network security. The ongoing evolution of 802.1X has cemented its place as a cornerstone of modern cybersecurity.
The Three Core Components of 802.1X
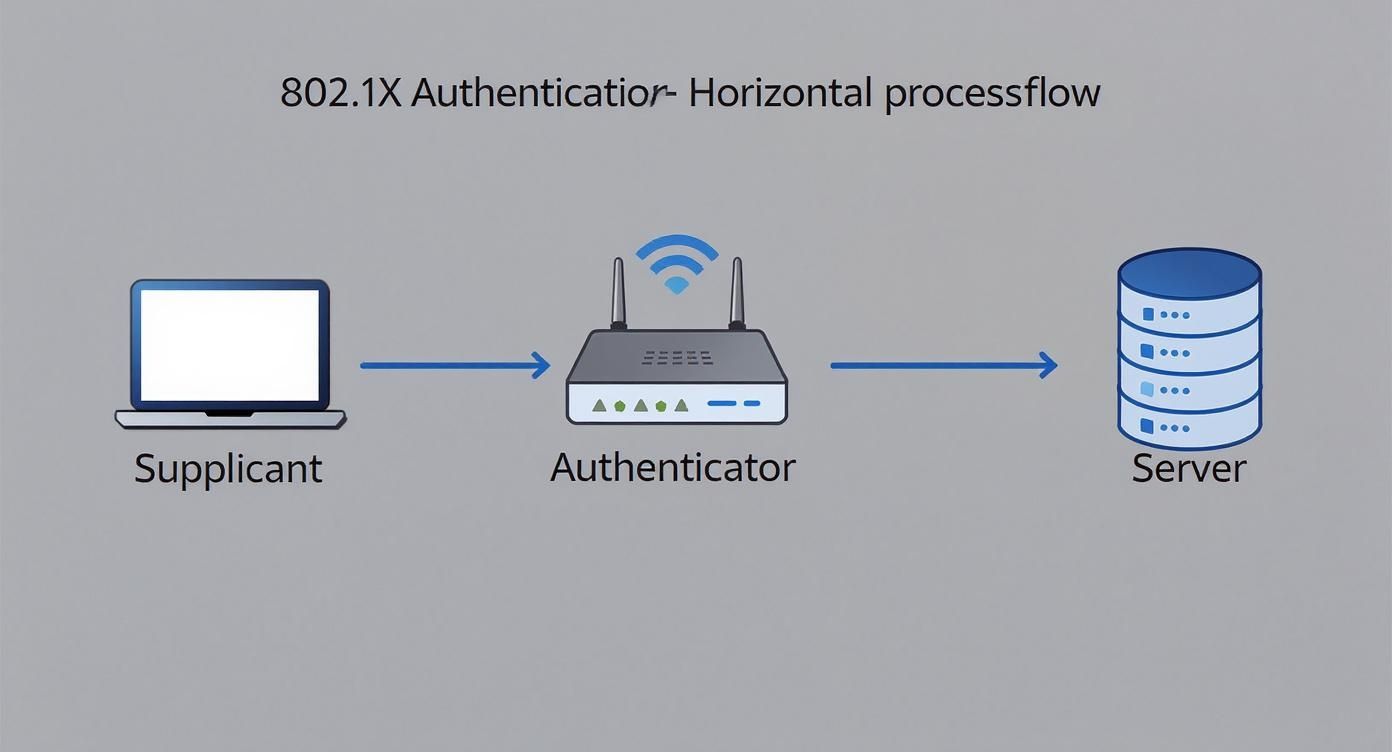
To really get a handle on 802.1X authentication, it helps to see it as a three-way conversation. Every time a device wants to join your network, three key players work together in a tightly choreographed sequence to verify its identity. Let's break down the team.
The Team Players
First, you have the Supplicant. It’s just a fancy name for the end-user device trying to get online—a company laptop in a BYOD Corporate setting, a student’s phone in Education, or even a point-of-sale terminal in Retail. The supplicant is the one asking for access and holds the credentials needed to start the process.
Next in line is the Authenticator. This is your network hardware acting as the gatekeeper, like a Cisco Meraki access point or switch. Its job isn't to make the final yes-or-no decision. Instead, it acts as a go-between, intercepting the supplicant’s request and passing it along for verification before opening up the port.
Finally, we have the Authentication Server. This is the brains of the whole operation. In nearly every case, this role is filled by a RADIUS (Remote Authentication Dial-In User Service) server. The RADIUS server maintains the central database of all approved users, devices, and their specific access policies. It’s the ultimate authority that gives the final thumbs-up or thumbs-down.
The Bouncer at the Club Analogy
Think of your network as an exclusive club. Your laptop (the Supplicant) shows up at the door wanting to get in. The bouncer (the Authenticator, your Meraki AP) stops you and asks for your ID.
The bouncer can't possibly know every single person on the guest list, so they radio the club manager inside (the Authentication Server). The manager cross-references your ID with the official guest list and confirms you meet the club's entry rules. Once confirmed, the manager radios back, "They're clear, let them in!" Only then does the bouncer unclip the velvet rope and grant you access.
Why a Centralized Brain Matters
This division of labor is precisely what makes 802.1X so effective, especially for sprawling networks in schools or large companies flooded with personal devices. By using a RADIUS server, you centralize all your authentication rules. This means network admins can manage access policies for thousands of users from a single point. It's how you grant segmented access—giving different users different levels of permission.
This centralized model means you can create distinct rules for different user groups. For instance, students might get access only to online libraries and learning portals, while faculty can access sensitive administrative systems—a world away from the "one password for everyone" approach.
For a deeper dive into how Cisco implements this, you can discover comprehensive insights on Cisco 802.1X for security experts.
Modern systems have built on this powerful foundation to smooth out the user experience. Instead of clunky logins, a Captive Portal can handle a simple, one-time authentication. From there, the system can automatically assign a unique, highly secure pre-shared key to each device using methods like IPSK (or EasyPSK). This approach strikes the perfect balance between robust security and simple management. You can see how this works by exploring a Cisco Meraki RADIUS server with group policy support.
How EAP and RADIUS Create a Secure Handshake
Okay, so we have our three key players: your device (the Supplicant), the access point (the Authenticator), and the RADIUS server. Now, let's look at how they actually communicate to verify who you are. This entire process hinges on two protocols working in tandem: the Extensible Authentication Protocol (EAP) and RADIUS.
Think of EAP as the specific language used for the identity check. It's a flexible framework, not a single method. This means it can support everything from simple password checks to highly secure digital certificates, much like a bouncer might accept a driver's license, a passport, or a military ID to grant entry.
RADIUS, on the other hand, is the armored truck that transports the conversation. It securely carries the EAP messages between the Cisco Meraki access point and the central authentication server. The access point itself is just a middleman; it never gets to see the sensitive credentials inside the package. It just passes the encrypted messages along.
This flow creates a secure digital handshake that verifies your identity without ever exposing your credentials over the airwaves.
As you can see, the authenticator's job is to act as a secure go-between, making sure the real verification only happens on the trusted authentication server.
The Step-by-Step Handshake
This whole back-and-forth happens in a matter of seconds. Here’s a play-by-play of what’s going on under the hood when you connect to a network using 802.1X authentication:
- Initiation: You try to connect to the Wi-Fi. The Cisco access point immediately puts your device in a "penalty box," blocking all network traffic except for authentication attempts. It then sends an "EAP-Request/Identity" message to your device, basically asking, "Who are you?"
- Response: Your device sends back its identity, like a username. This isn't your password, just the login name.
- Relay: The access point takes this response, wraps it inside a RADIUS packet, and shoots it over to the RADIUS server.
- Challenge: The RADIUS server looks up the username and, based on the network's security policy, initiates a challenge. It sends this challenge back through the access point to your device.
- Proof: Your device responds to the challenge with its credentials—this could be a securely hashed password or a digital certificate. This is the real proof of identity.
- Verification: The proof is relayed back to the RADIUS server, which does the heavy lifting of validating the credentials.
- Success or Failure: The server makes its decision. If everything is correct, it sends a "RADIUS Access-Accept" message. If not, it's an "Access-Reject."
- Connection Granted: When the access point gets the "Access-Accept" green light, it opens the floodgates and grants your device full access to the network.
The most critical part of this entire exchange is that the access point never sees your password. It only ever acts as a secure pass-through, which is a cornerstone of the 802.1X security model.
Picking the Right EAP Method
Because EAP is a framework, you have to choose a specific "flavor" or method for your network. The one you pick depends on your security needs, the types of devices connecting, and how you manage user credentials. Some methods are great for corporate laptops, while others are better suited for guest devices.
Here's a quick look at some of the most common EAP methods and where they fit best.
Comparing Common EAP Authentication Methods
| EAP Method | Security Level | Credential Type | Common Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| EAP-TLS | Very High | Digital Certificates | Corporate-owned devices, IoT, high-security environments |
| EAP-TTLS | High | Username/Password | BYOD, university networks where users bring their own devices |
| PEAP | High | Username/Password | Most common for enterprise Wi-Fi, supported by most devices |
| EAP-FAST | High | Protected Access Credentials (PAC) | Cisco environments, helps speed up re-authentication |
| EAP-MD5 | Low | Username/Password | Legacy method, not recommended for new deployments |
Ultimately, the goal is to choose the method that offers the best balance of robust security and a smooth user experience for your specific environment. For most businesses today, PEAP and EAP-TLS are the go-to choices.
Authentication Solutions For Every Sector
This secure and flexible handshake is precisely why 802.1X is a favorite across so many different industries.
- In Education, it's used to automatically place students on a restricted network while giving faculty access to internal resources.
- In Retail, it locks down the network to ensure only authorized point-of-sale terminals and inventory scanners can connect, protecting sensitive payment data.
- For corporate BYOD programs, it's the gold standard for securely onboarding employee-owned devices without giving them free rein on the company network.
Modern authentication solutions have built on this rock-solid foundation to make things even easier. Technologies like IPSK and EasyPSK, for instance, can streamline the whole experience. A user might first connect to a branded Captive Portal, and the system automatically generates a unique key for their device in the background. The secure EAP and RADIUS handshake is still there, but it's completely invisible to the end-user.
There is a whole world of modern user authentication techniques available that use the 802.1X framework to perfectly balance tough security with simple, user-friendly access.
Moving Beyond Passwords with IPSK and Certificates
For years, the shared Wi-Fi password has been a necessary evil. You know the drill—a single password scrawled on a whiteboard, handed out on slips of paper, or emailed to new employees. While it seems simple, this approach is a massive security headache. Shared passwords get passed around, are rarely updated, and create a single point of failure that can expose your entire network.
This is a huge problem in dynamic environments. Think about Education, where new students arrive each semester. Or Retail, with constant staff turnover and point-of-sale systems needing secure connections. And for corporate BYOD (Bring Your Own Device) policies? Managing a sea of personal devices with one shared key is a logistical nightmare waiting to happen.
Thankfully, modern authentication solutions offer a much smarter path forward, one that leaves the single, shared key behind for good.
Introducing IPSK: A Unique Key for Every Device
One of the most effective and friendly methods is Identity Pre-Shared Keys (IPSK), sometimes called EasyPSK. Imagine giving every single user or device its own unique "password" to the Wi-Fi network, but without the administrative chaos. That’s exactly what IPSK delivers.
Instead of one key for everyone, IPSK generates a distinct key for each authenticated device. This offers some immediate, game-changing advantages:
- Individual Accountability: If a device is lost, stolen, or belongs to a departing employee, you just revoke its specific key. No one else on the network is affected.
- Enhanced Security: A compromised key only impacts a single device, not your entire infrastructure. The blast radius is contained.
- Simplified Management: IT teams can easily issue and revoke keys for individuals or groups, making it a perfect fit for managing messy BYOD environments.
Platforms like Splash Access make deploying IPSK on Cisco Meraki hardware incredibly simple. A new user can onboard their device through a user-friendly Captive Portal, and the system automatically generates and assigns a unique key behind the scenes. It's the perfect blend of high security and a friction-free user experience. You can learn more about how to combine IPSK with RADIUS authentication to build an even more powerful and scalable network.
The Gold Standard: Certificate-Based Authentication
For organizations demanding the absolute highest level of security, certificate-based authentication using EAP-TLS is the answer. This method ditches passwords entirely. Instead, a unique digital certificate is installed on each device. Think of it as a digital passport—nearly impossible to forge, steal, or guess.
The device presents its certificate to the network, which verifies it against a trusted authority before granting access. This is so powerful because it verifies the device itself, not just a password that someone happens to know.
With certificate-based authentication, you completely eliminate password-related risks. There are no credentials to be phished, stolen, or shared. It’s the foundational technology for building a true Zero Trust network environment where every connection is verified every time.
While it might sound complicated, modern management tools and platforms can automate the entire certificate lifecycle—from issuance and renewal to revocation. For corporate-owned devices in a Cisco environment, deploying certificates ensures that only company-approved hardware can access sensitive internal resources. This level of control is essential for industries handling sensitive data, like healthcare or finance.
By ditching shared passwords for these advanced authentication solutions, organizations can build a network that is not only more secure but also far easier to manage at scale.
Rolling Out 802.1X on Cisco Meraki Networks
Let's be honest, the thought of setting up a full 802.1X authentication system can seem pretty intimidating. Traditionally, it was a job that demanded deep technical knowledge and long hours of painstaking configuration.
Fortunately, that's no longer the case for anyone running on Cisco Meraki hardware. When you pair Meraki’s cloud-managed networking with a smart authentication solution, the whole process becomes surprisingly simple. Enterprise-grade security is no longer a complex puzzle reserved for big IT departments.
Making Onboarding Effortless with Captive Portals
One of the biggest challenges with any secure network is the user experience. You need top-notch security, but you can’t make the login process so difficult that it frustrates everyone. This is exactly where modern tools like Splash Access, especially on Cisco gear, make a huge difference.
Instead of putting users through a complicated setup, you can greet them with a clean, branded Captive Portal for a quick, one-time enrollment. It’s a game-changer.
This approach works beautifully in all sorts of environments:
- Education: A new student arrives on campus, connects to an onboarding Wi-Fi, and logs in through the school's portal just once. Their device is then automatically set up with secure credentials for the entire year. No more helpdesk calls.
- Retail: Need to get seasonal workers online quickly and securely? They can just log in through the portal, and their device is granted access for as long as they're employed. IT doesn't have to touch a thing.
- Corporate BYOD: A new employee can connect their personal laptop or phone by following a simple, guided process. Their device is checked for compliance and securely configured from the moment they join.
Seamless Integration and Management
The real beauty of using a platform like Splash Access is how tightly it integrates into the Meraki dashboard. You don’t have to juggle different systems or manage separate user databases. Everything is right there in a single, familiar interface.
The screenshot below gives you a glimpse of just how straightforward it is. You can manage all your network access policies in one place.
This unified management is what turns a once highly complex task into something manageable, making robust security a realistic goal for almost any organization.
Behind the scenes, the system is doing all the heavy lifting. It automates credential management, whether that means assigning unique IPSK keys or deploying digital certificates based on a user's role. For instance, a student might get an EasyPSK key for the campus Wi-Fi, while a professor’s device gets a certificate that unlocks access to sensitive internal servers.
This level of automation doesn't just save IT staff countless hours; it also slashes the risk of human error. Policies are applied correctly and consistently every single time a new device connects, keeping your security posture solid.
If you're looking to build a secure network from scratch, getting the fundamentals right is key. A great place to start is by checking out guides on the installation of wireless networks that use these modern techniques. By combining Cisco Meraki hardware with an intelligent authentication solution, you get a powerful, scalable, and user-friendly way to lock down any network.
Why 802.1X Is a Must-Have for Modern Network Defense
In a world where every device is a potential doorway for threats, a simple Wi-Fi password just doesn't cut it anymore. That's where 802.1X authentication comes in. Think of it as your network's highly-trained security guard, checking the ID of every single person and device trying to get in.
It’s more than just a fancy tech standard; it’s a fundamental shift in how we secure networks. It moves beyond asking "what's the password?" to demanding a much more important question: who and what are you, and are you allowed to be here?
Build Smarter, Safer Networks with Segmentation
One of the biggest wins you get from implementing 802.1X, especially with gear from vendors like Cisco and Meraki, is the power of network segmentation. This is just a technical way of saying you can divide your network into smaller, isolated zones. If a fire breaks out in one room, firewalls keep it from spreading to the whole building—segmentation does the same for your network.
Imagine how this works in a school:
- Students connect and get access to the internet and learning tools, but nothing else.
- Faculty are on a separate slice of the network with access to grade books and internal servers.
- Guests who sign in through a Captive Portal are put in their own sandboxed area, safely away from any sensitive data.
This isn't just for schools. A Retail store can keep its critical point-of-sale terminals completely isolated from the free guest Wi-Fi. In a corporate BYOD environment, personal phones and laptops can be kept on a separate network from company-owned machines that hold sensitive data.
By verifying every connection at a central point, 802.1X gives IT teams a single dashboard to manage access. It stops being about just opening a gate and becomes more about intelligently directing traffic where it's supposed to go.
Get a Crystal-Clear Audit Trail for Compliance
Beyond just keeping bad actors out, 802.1X delivers something that every IT manager and compliance officer dreams of: a perfect audit trail. Every single connection attempt is logged and tied to a specific user or device identity.
This means you always know exactly who connected, from what device, and at what time. This level of detail is non-negotiable for meeting strict compliance standards like PCI DSS or HIPAA. And if something does go wrong, this trail is your first and best tool for forensic analysis.
Modern authentication solutions take this even further. With technologies like IPSK (also known as EasyPSK), every single device gets its own unique pre-shared key. Now, instead of just seeing that a user logged in, you can trace network activity all the way back to a specific company laptop or a particular smartphone. This transforms security from a reactive chore into a proactive strategy, making 802.1X an absolutely essential part of any modern network defense.
Your 802.1X Questions, Answered
Let's tackle some of the most common questions that come up when people first look into 802.1X authentication. Getting these fundamentals down can make all the difference when deciding if it's the right move for your organization.
Isn't 802.1X Overly Complicated for a Small Business?
In the past, that was a fair criticism. But times have changed. Modern authentication solutions, especially those built for hardware from companies like Cisco Meraki, have done away with the heavy lifting.
What once required a dedicated IT team can now be managed through user-friendly platforms. This brings top-tier, enterprise-grade security within reach for almost any organization.
How Does 802.1X Fit in with a Captive Portal?
They actually complement each other beautifully, allowing you to tailor the network experience for different users. You can use 802.1X for your primary, high-security network—perfect for company-owned devices or in corporate BYOD and education environments.
At the same time, you can set up a separate guest network that uses a simple Captive Portal. Visitors get a straightforward login, which can then trigger an automated IPSK or EasyPSK assignment behind the scenes, keeping them securely isolated from your main network.
The real magic here is flexibility. You can have a seamless, certificate-based connection for your staff and a simple, branded portal for guests, all running on the same Cisco Meraki infrastructure.
What’s the Big Deal? Isn’t 802.1X Just a Fancy Wi-Fi Password?
Not at all. A standard Wi-Fi password (the kind you see with WPA2/3-Personal) is a single, shared secret. Once that password is out, anyone who has it can get on your network, and you have no way of knowing who is who. If it leaks, your entire network is wide open.
With 802.1X authentication, every user and device gets its own unique set of credentials. This is a massive security upgrade. It means you have individual accountability and can grant or revoke access on a per-user basis—an essential capability for security-conscious sectors like retail and healthcare.
Ready to leave shared passwords behind and secure your network properly? Splash Access provides a powerful platform that simplifies deploying robust 802.1X and IPSK solutions on your Cisco Meraki network. Learn more about our advanced authentication solutions.